The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Enclosure Hinges: Selection, Materials, and Applications
In the fields of industrial manufacturing and electrical engineering, industrial enclosure hinges are more than just simple connection points. In fact, it is a core component that maintains the integrity of an industrial enclosure. However, choosing the wrong hinge can lead to serious consequences.
For instance, if a hinge fails, the door panel will sag. Consequently, this door sag prevents the gasket from compressing correctly. When the seal fails, moisture, dust, and corrosive chemicals can breach the interior of the cabinet. Ultimately, this directly compromises the cabinet’s IP Rating (e.g., IP65, IP66) or NEMA Rating (e.g., NEMA 4, NEMA 4X).
More specifically, the consequences include:
- Short circuits in sensitive electronic components due to moisture.
- Control panel overheating caused by dust accumulation.
- Operator injury resulting from heavy doors detaching.
In environments such as chemical plants, food processing facilities, or outdoor telecommunications base stations, hinges must withstand extreme physical and environmental stress. Therefore, this article provides a selection guide based on engineering data to help engineers and procurement specialists make the right decision.
Types of Industrial Enclosure Hinges
Broadly speaking, industrial hinges are primarily categorized into four types based on mounting methods, functionality, and security requirements.
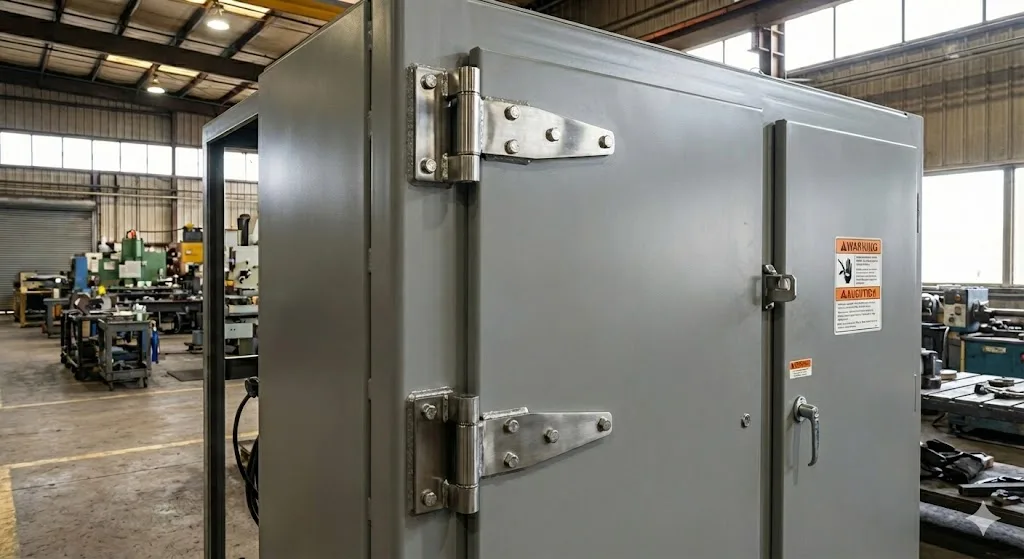
External Hinges

Over-Center Compression Latch and Heavy-Duty Hinge – Video Demo
External hinges are mounted on the outside of the enclosure door. Currently, this is the most common type of industrial hinge.
- Technical Features:
- Opening Angle: Notably, it allows for 180° to 270° opening angles. This provides maximum operating space for technicians.
- Installation: Mounted directly to the door frame surface using screws or welding.
- Cost: Generally, it has a simple structure with relatively low manufacturing costs.
- Applicable Scenarios:
- Standard electrical panels.
- General-purpose indoor mechanical enclosures.
- Non-high-security environments.
- Limitations: However, because the hinge is exposed, it is susceptible to removal or tampering, making it unsuitable for high-security areas.
Concealed / Internal Hinges
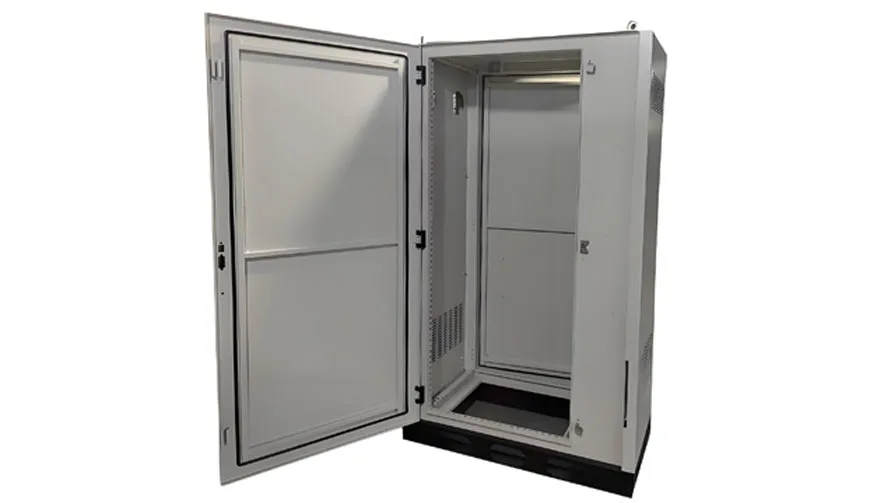

Video demonstration of Concealed / Internal Hinges applications
In contrast to external models, concealed hinges are installed inside the door and frame. When the door is closed, the hinge is not visible from the outside.
- Technical Features:
- Security: Since the pin or screws are inaccessible from the outside, it offers extremely high resistance to tampering. Thus, this is the top choice for Secure hinges for vandal-proof enclosures.
- Sealing: Furthermore, this design makes it easier to maintain a continuous seal on the cabinet exterior, aiding in compliance with NEMA 4 and IP66 standards.
- Opening Angle: On the downside, due to internal structural limitations, the opening angle is usually restricted to between 90° and 120°.
- Applicable Scenarios:
- Outdoor telecommunications cabinets.
- Server racks.
- Electrical facilities located in public areas.
Continuous / Piano Hinges

Alternatively, continuous hinges cover the entire height of the door.
- Technical Features:
- Load Distribution: Crucially, weight is evenly distributed along the entire door frame rather than being concentrated on two or three points. This significantly reduces stress per unit area.
- Durability: This design prevents the door panel from warping or sagging.
- Alignment: Additionally, it maintains continuous contact between the door and the frame, aiding in the compression of long sealing strips.
- Applicable Scenarios:
- Heavy-duty industrial doors.
- High-vibration environments (e.g., generator set enclosures).
- Heavy-duty tool cabinets.
Torque and Positioning Hinges
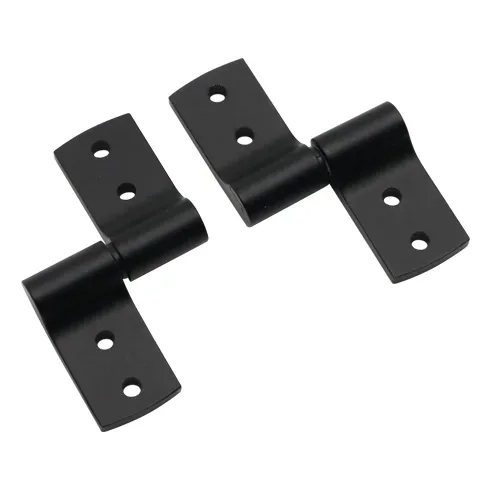

Installation & Application Demo: Torque and Positioning Hinges
Finally, these hinges utilize friction or mechanical structures to control the movement of the door.
- Technical Features:
- Infinite Positioning: Users can hold the door or panel at any angle. As a result, no additional gas springs or support stays are required.
- Safety: Moreover, it prevents heavy panels from accidentally falling and injuring personnel due to gravity during maintenance.
- Keyword Coverage: These products are often searched for as Hinges that hold open.
- Applicable Scenarios:
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI) display mounts.
- Medical equipment control panels.
- Lids or covers requiring frequent access for maintenance.
Lift-off Hinges
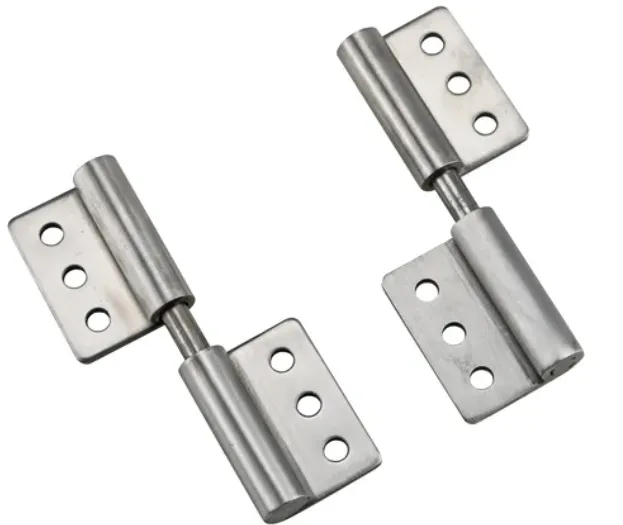

Lift-Off Hinges – Installation and Application Demonstration
- Technical Features: Consists of male and female parts, allowing the user to simply lift the door panel up and remove it after opening.
- Applicable Scenarios: Specifically, narrow passageways or space-constrained server rooms where the door panel needs to be completely removed to facilitate maintenance.
Material Selection: Matching the Environment
Fundamentally, the choice of material determines the lifespan of the hinge. Materials must be selected based on the chemical and physical characteristics of the application environment.
304 vs. 316 Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is the standard material in the industrial sector, offering high strength and corrosion resistance.
- 304 Stainless Steel (ASTM A240 Type 304):
- Characteristics: Contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel. Overall, it has good corrosion resistance and formability.
- Applications: Indoor food processing, general chemical environments, washdown areas.
- 316 Stainless Steel (ASTM A240 Type 316):
- Characteristics: However, Type 316 has added 2% Molybdenum. This gives it extreme resistance to chlorides and salt spray.
- Applications: Marine environments, offshore oil rigs, coastal infrastructure, pharmaceutical plants.
- Data Reference: Notably, in ASTM B117 salt spray tests, 316 stainless steel performs significantly better than 304.
Zinc Die-Cast
Alternatively, zinc alloys are manufactured via die-casting, offering extremely high dimensional precision.
- Characteristics:
- Strength: High tensile strength, suitable for medium loads.
- Finish: However, it must be chrome-plated or black powder-coated to prevent oxidation.
- Cost: Typically, it is more cost-effective than stainless steel.
- Applications: Indoor electrical cabinets, IT cabinets, general mechanical equipment.
Thermoplastic and Glass-filled Nylon
- Characteristics:
- Corrosion Resistance: Naturally immune to most acids, alkalis, and solvents. In short, it will not rust.
- Weight: More than 50% lighter than metal.
- Insulation: Non-conductive material, increasing electrical safety.
- Standard Reference: Materials complying with UL 94-V0 flammability standards should be selected.
- Applications: HVAC systems, corrosive chemical storage cabinets, light-duty access doors.
Selection Criteria: Expert Checklist
To ensure success, verify the technical parameters against the following checklist before purchasing hinges.
Load Bearing Capacity & Safety Factor
First and foremost, do not guess the weight of the door. Specific values must be calculated.
- Calculation Formula: Total Door Weight = Weight of the Door Panel + Weight of Equipment mounted on the door (e.g., fans, meters, cables).
- Safety Factor: Furthermore, it is recommended to reserve a 25% – 30% safety margin. If the total door weight is 40kg, choose a hinge combination rated for at least 50kg.
- Distribution: Also, increasing the distance (spacing) between hinges improves door stability and reduces side-loading on the hinge pins.
Sealing & IP Rating
Next, the hinge installation method must not compromise the enclosure’s protection rating.
- Outdoor Applications: You must use Waterproof hinges for outdoor enclosures.
- Compliance:
- For IP65/IP66 cabinets, hinges must be equipped with O-rings or sealing gaskets to prevent water from seeping through screw holes.
- Conversely, for NEMA 4X enclosures, 316 stainless steel hinges must be used, and mounting holes must be sealed.
- Reference Standard: UL 50E (Enclosures for Electrical Equipment).
Opening Angle & Space Constraints
- 90° Limit: Suitable for cabinets placed against a wall.
- 120° Limit: Often common in concealed hinges to prevent the door from hitting adjacent equipment.
- 180° – 270°: Suitable for areas with wide aisles, especially when the internal backplane needs to be fully exposed for wiring operations.
Mounting Styles
- Screw-on: Easiest for replacement and maintenance. Requires pre-drilled holes.
- Weld-on: Permanent fixture. While it offers the highest strength, it cannot be adjusted after installation. Common on heavy-duty steel cabinets.
- Snap-in: Used for sheet metal cabinets; allows quick, tool-free installation. Although suitable for mass production, it has lower load-bearing capacity.
Common Industrial Application Case Studies
Outdoor 5G Telecom Base Station Cabinet
- Environmental Challenge: Equipment is installed in coastal areas, facing high humidity, salt spray corrosion, heavy rain, and potential vandalism risks. Additionally, there are large temperature variations (-20°C to +50°C).
- Selection Recommendation: 316 Stainless Steel Concealed Hinges.
- Reasoning:
- 316 Stainless: Resists salt spray corrosion, meeting ASTM B117 test requirements.
- Concealed Design: Prevents prying, thereby enhancing security.
- Internal Installation: Protects the hinge pivot from direct rain exposure, ensuring IP55 or IP65 ratings remain intact.
CNC Machine Control Cabinet
- Environmental Challenge: The workshop contains significant oil mist and metal chips. Simultaneously, the equipment generates continuous high-frequency vibration during operation. A heavy industrial monitor is mounted on the door.
- Selection Recommendation: Heavy-duty Zinc Die-cast Continuous Hinge or Reinforced External Hinge.
- Reasoning:
- Continuous Hinge: Full-length support effectively distributes the weight of the monitor, thus preventing the door panel from sagging due to vibration.
- Vibration Resistance: The continuous pin design is more resistant to loosening caused by long-term vibration compared to single-point hinges.
FAQ
Q: Which hinge is best for outdoor enclosures? A: Generally, for outdoor enclosures, 316 stainless steel hinges should be the primary choice to prevent rust. To achieve NEMA 4X or IP66 protection ratings, it is recommended to use external hinges with sealing gaskets or, alternatively, concealed hinges mounted internally to minimize leak points.
Q: How do I measure industrial hinges? A: Key dimensions include: 1. Leaf length; 2. Leaf width; 3. Pin diameter; 4. Knuckle length. However, for replacements, you must ensure the hole spacing matches strictly.
Q: What is the difference between 304 and 316 stainless steel hinges? A: The main difference lies in the chemical composition. 316 stainless steel contains Molybdenum, which makes its corrosion resistance significantly higher than 304 stainless steel. Therefore, in marine environments or environments exposed to chlorides, 316 stainless steel must be used.
Q: What is a torque hinge, and when do I need it? A: A torque hinge features internal resistance that can hold a door in any position. In other words, if you need a monitor, lid, or control panel to hover at a specific angle for easy operation and do not wish to use gas struts, you need a torque hinge.
Conclusion
In summary, selecting the right industrial enclosure hinges is a crucial step in ensuring the long-term stable operation of equipment. This decision directly impacts the equipment’s protection rating (IP/NEMA Rating), operational safety, and maintenance costs.
- For high-corrosion environments, stick to 316 Stainless Steel.
- Conversely, for high-security requirements, choose Concealed Hinges.
- For heavy loads, Continuous Hinges are the best choice.
Finally, always refer to relevant technical standards (such as UL 50E and IEC 60529) for verification.
Call to Action: Don’t let the wrong hardware compromise your engineering design. Contact our engineering team today for a free selection consultation, or download our latest Industrial Hinge Product Catalog (PDF) to view detailed load data and dimensional drawings for every model. Ensure your next project meets the highest industrial standards.