Industrial Removable Pin Hinges: Procurement Guide & Benefits (ANSI/ASTM)
In the world of industrial hardware, Removable Pin Hinges (also known as loose pin, slip joint, or take-apart hinges) are a staple configuration for heavy-duty equipment doors, control cabinets, and inspection panels.
While fixed-pin hinges are often the default for maximum security, removable pins are a strategic choice for Operational Efficiency and Serviceability.
For Procurement Managers, choosing the right removable pin hinge isn’t just about hardware specs—it’s about lowering the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). It means faster assembly lines, reduced maintenance downtime for your end-users, and a simplified spare parts inventory strategy.
This guide analyzes the technical advantages, application scenarios, and selection criteria based on ANSI/BHMA and ASTM standards to help you make the right sourcing decision.
What is a Removable Pin Industrial Hinge?
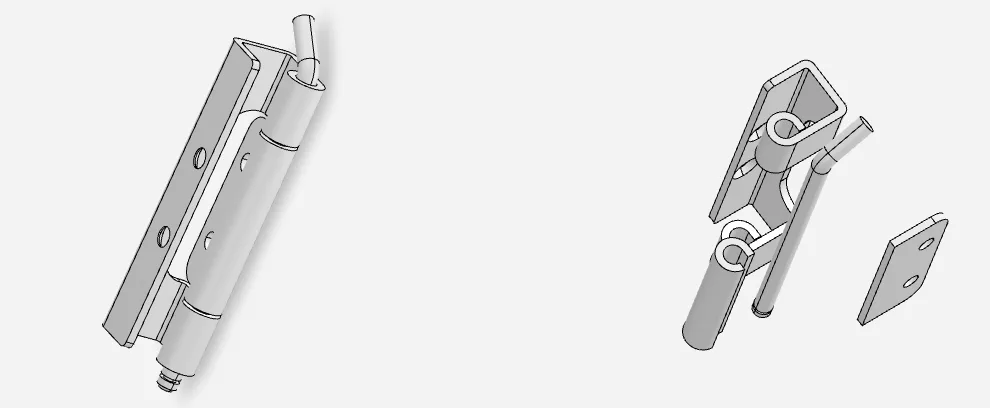

A removable pin hinge features a pivot pin that can be extracted while the hinge is installed, allowing the door or panel to be completely separated from the frame without unbolting the hinge leaves.
Critical Components & Standards (Risk Control)
To ensure supply chain consistency, it is vital to specify components against recognized standards:
- Leaves (Structural Integrity): The load-bearing plates. We strictly recommend sourcing hinges that certify to material specifications like ASTM A240 (e.g., 304/316 Stainless Steel).
- Procurement Note: Compliance with ASTM ensures batch-to-batch consistency, preventing the “hidden cost” of receiving inferior mixed-metal lots that corrode prematurely.
- Pin (Shear Strength): The axis bearing the load. Precision in diameter and straightness is vital to prevent seizing.
- Bushings/Bearings (Longevity): Essential for high-cycle applications to reduce friction. We recommend specifying performance grades aligned with ANSI/BHMA A156.1 to ensure the hinge lasts as long as the machine itself.
Common Pin Configurations

To balance “removability” with “safety,” industrial hinges use several pin retention methods:
- Straight Pin: Held by gravity or friction. Fast removal but sensitive to vibration.
- Retaining Ring (Clip): Limits axial movement; suitable for transport vibration.
- Threaded/Locking End: Uses a threaded cap or set screw. Best for high-vibration environments requiring occasional maintenance.
- Safety/Cotter Pin: Features a cross-hole for a cotter pin, offering a visual safety check.
Tip: Need a specific pin retention method for a new project? We can often customize the pin style (e.g., adding a retaining ring groove) without re-tooling the entire hinge leaf, saving you significant NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs.
The Engineering Case: Why Use Removable Pins?
The decision to use removable pins is an engineering trade-off prioritizing Maintenance Speed and Assembly Flexibility.
Minimizing Downtime & Maintenance Steps
In 24/7 production environments, every minute of downtime costs money. Removable pins compress the door removal process significantly:
- Standard Hinge: Unscrew 12+ bolts → Risk of lost hardware/stripped threads → Remove Door.
- Removable Pin: Extract Pin → Lift Door.
This reduces the “Mean Time to Repair” (MTTR) for internal component replacement or cleaning, a key metric for your end-customers.
Modular Assembly & Logistics Optimization
For large machinery and modular cabinetry, removable pins offer distinct logistical advantages:
- Transport Safety: Doors can be shipped separately from frames to prevent hinge damage or glass breakage during transit.
- Warehouse Optimization: You can stock doors and frames separately, optimizing your warehouse space and reducing inventory damage rates.
- Ergonomics: Installers can mount light hinge leaves first, then hang heavy doors later, improving safety.
Component Lifecycle Management
In high-cycle applications (reference ANSI/BHMA A156.1 cycle classes), wear concentrates on the pin and bushing. Removable designs allow for replacing just the pin rather than the entire welded hinge assembly. This significantly reduces long-term spare parts costs and simplifies your after-sales support.
Removable Pin vs. Fixed Pin: Selection Comparison
Use this table to determine the correct hinge type for your application.
| Feature | Removable Pin Hinge | Fixed Pin / Riveted Hinge |
| Primary Value | Speed of Maintenance & Assembly | Security & Vibration Resistance |
| Door Removal | Instant (Pull pin) | Slow (Unbolt leaves) |
| Security Risk | Medium (Unless safeguarded) | High (Tamper-resistant) |
| Vibration | Requires anti-detach mechanism | Naturally resistant |
| Best For | Inspect Panels, Production Lines, HVAC | Exterior Security Doors, High-Vibration |
| Standard Ref. | ANSI/BHMA A156.1 Options | ANSI/BHMA A156.1 General |
Typical Application Scenarios

Industrial Enclosures & NEMA Cabinets
- Scenario: Electrical control panels requiring regular wiring updates.
- Standard: Refer to UL 50E for environmental resistance.
- Value: Ensuring hinge materials match the enclosure’s rating (e.g., NEMA 4X or IP65) prevents expensive water damage claims.
Machine Guarding & Safety Gates
- Scenario: Protective covers on automated lines that need removal for tool changes.
- Standard: If the guard is part of a safety interlock system, hinge selection must align with ISO 14120 (Guards) and risk assessments under ISO 12100.
Food Processing & Cleanrooms
- Scenario: Equipment requiring aggressive wash-downs.
- Requirement: AISI 316 Stainless Steel is mandatory.
- Value: 316 grade withstands caustic cleaners without pitting. Pitting causes pins to seize, which defeats the purpose of a removable hinge.
Technical Selection Guide (Procurement Checklist)
To ensure supplier consistency and engineering validation, specify these parameters.
Load Capacity & Sizing
Undersized hinges lead to door sagging; oversized hinges waste budget.
- The Challenge: Calculating the exact moment load based on door width, height, and weight can be complex.
- How We Help: You don’t need to be a physicist. Simply send us your door dimensions and weight. Our engineering team will run the calculation against ANSI Grade standards and recommend the most cost-effective hinge count and positioning for your project.
Environmental Corrosion Resistance
Avoid vague terms like “rust-proof.” Define the finish based on standardized tests to ensure vendor accountability:
- Salt Spray Test: Specify hours (e.g., 96h, 500h) referencing universal standards like ASTM B117 or ISO 9227.
- Classification: Use EN 1670 grades (e.g., Grade 4 for high corrosion resistance) to clarify expectations for suppliers.
Anti-Vibration & Retention
If the equipment vibrates (generators, compressors), a simple straight pin is unsafe.
- Requirement: Explicitly request “Vibration-proof retention” in your RFQ (e.g., E-clips, Nyloc nuts, or Safety Wire holes).
Installation & Maintenance Best Practices
Alignment is Critical
For removable pins to function, coaxial alignment is non-negotiable. Misaligned hinges create shear stress that binds the pin, making “removability” impossible.
- Tip: Use laser alignment tools for heavy doors during the QC process.
Lubrication Protocol
Even stainless steel can gall (cold weld).
- Maintenance: Apply a lithium-based grease or PTFE lubricant to the pin quarterly. This ensures the withdrawal force remains within manual operation limits.
FAQ
Q: Are removable pin hinges secure?
A: Standard loose pin hinges are not high-security. For exterior doors, specify NRP (Non-Removable Pin) options (locked via set screw) or mount hinges internally.
Q: Can I use them in corrosive environments?
A: Yes, but material selection is key. Specify 316 Stainless Steel and verify passivation. Refer to ASTM B117 test reports to confirm coating quality for non-stainless options.
Q: How do I prevent the pin from falling out due to vibration?
A: Never use gravity-held straight pins on vibrating machinery. Specify hinges with Retaining Rings (Circlips) or Threaded Ends to mechanically lock the pin in place.
Q: What is the load difference compared to fixed hinges?
A: Structurally, they are similar if the pin diameter and material are identical. However, removable pins have microscopic clearance, which can increase wear over time. Ensure sizing includes a safety factor of 2.5:1.
Ready to Optimize Your Hardware Selection?
Standardizing on the right removable pin hinge can streamline your production and delight your service teams. However, balancing load capacity, environmental resistance, and cost requires expert insight.
Don’t navigate the catalog alone. Contact our engineering team today for a free consultation on your current enclosure design, or request a sample kit to see the difference in quality firsthand.