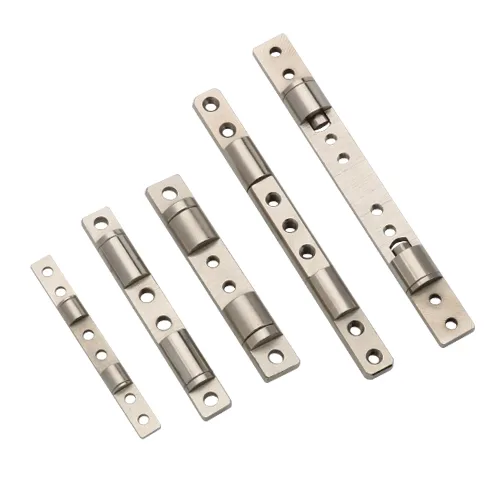
Industrial Stop Hinges (Integrated Stops): A Safety & Selection Guide for Equipment
Introduction: The Background of Limit Requirements in Industrial Scenarios
In industrial equipment and vehicle applications, moving doors, lids, or hatches present serious safety hazards when they lack stop functionality—this is exactly what stop hinges are designed to provide.
- Vehicle Case: Once a car door check (limiter) fails, vibration and jolts during driving can cause the door to shake or even open accidentally, creating a severe risk of ejecting passengers from the vehicle.
- Equipment Case: In factory cabinets or medical equipment, if a free-swinging door or lid opens excessively, it may collide with adjacent equipment and poses a risk of pinching operators.
These potential accidents prompt engineers to introduce the “Safety Stop“ feature in hinges during the initial design phase. Its core purpose involves limiting the hinge’s rotation angle, mechanically preventing collisions and injuries caused by excessive opening and closing.
This approach also aligns with international safety standards (such as ISO 12100:2010), which emphasize actively identifying and eliminating mechanical motion risks during the design phase. Therefore, safety stop hinges now represent a critical detail for ensuring safety and equipment integrity in fields such as industrial cabinets, medical instruments, and automotive doors.
Collision Prevention, Seal Protection, and Structural Fatigue Reduction
An integrated stop hinge acts as more than just a connector; it serves as a core component of the equipment protection system.
Collision Prevention
By limiting the maximum opening angle of the door panel, the stop function effectively avoids the door body striking adjacent cabinets, walls, or equipment enclosures.
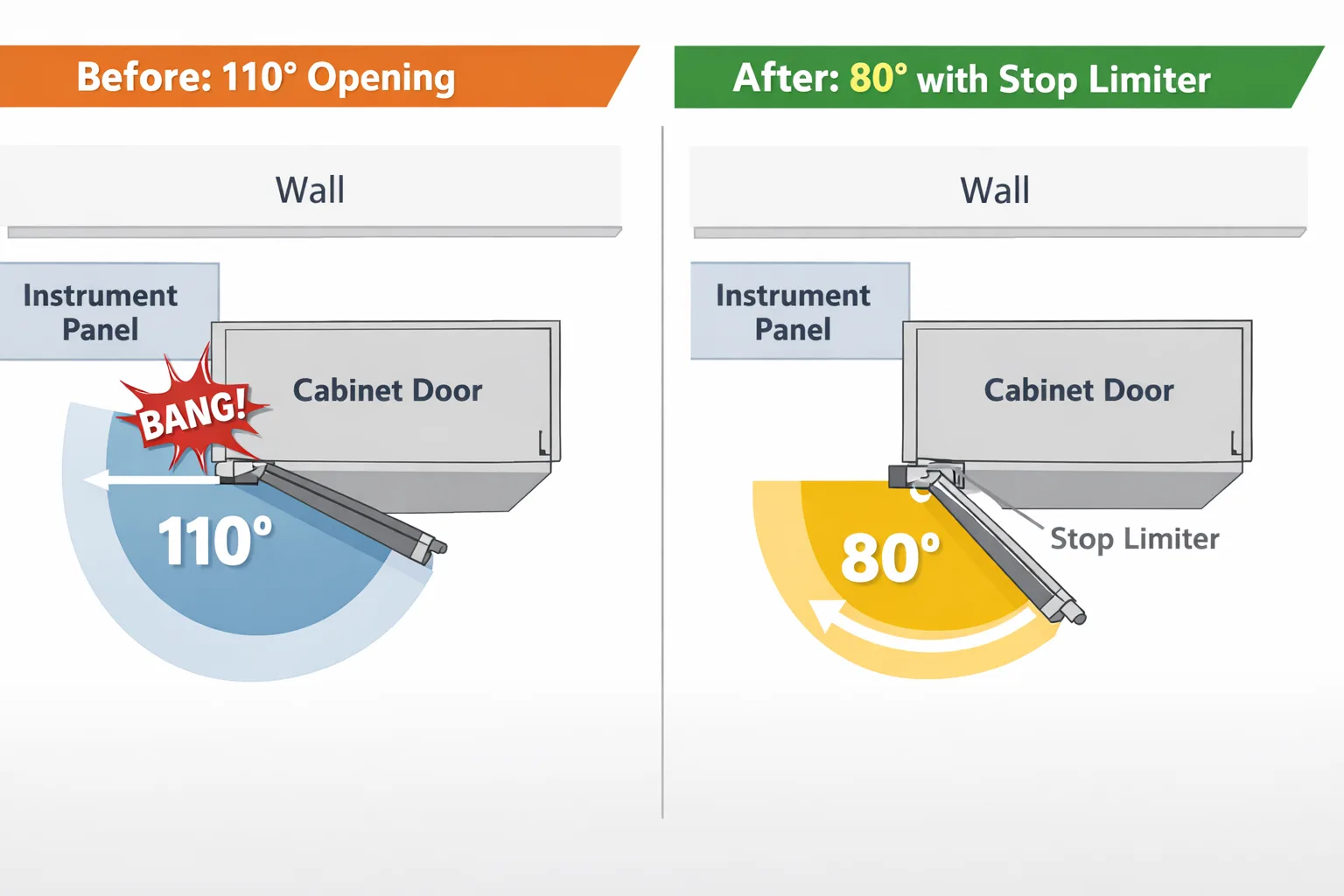
- Application Example: Certain power distribution cabinet hinges feature built-in stops that forcibly limit the original 110° opening angle to 80°.
- Effect: Prevents the cabinet door from scraping against adjacent instrument panels or walls when opened excessively.
Seal Protection
Stop functionality proves crucial for maintaining IEC 60529 (IP Dust and Water Protection Ratings).
- Principle: When hinges control a lid to open or close within a reasonable range, the system avoids placing excessive stress, such as crushing or pulling, on the sealing strip.
- Risk: Research indicates that when a vehicle door check fails (e.g., a dislodged door check), the door may fail to latch when closed and may not operate as intended; therefore, proper stop/check functionality is a prerequisite for ensuring consistent closure and the compression conditions required for sealing (water/dust ingress protection).
Fatigue Reduction and Shock Absorption
Compared to direct collisions without cushioning, hinges with soft stops or damping mechanisms offer significant advantages:
- Buffering Mechanism: Decelerates the door as it approaches the limit position, avoiding forceful impact against the frame.
- Life Extension: This soft-stop design reduces the stress of repeated impact on the hinge pin and cabinet connections. Long-term use reduces metal fatigue and loosening, thereby extending equipment life and lowering maintenance costs.
Enhancing Operational Safety
Pinch Point Control
The mechanical design standard ISO 13854 explicitly stipulates the minimum gap requirements needed to avoid crushing human body parts.
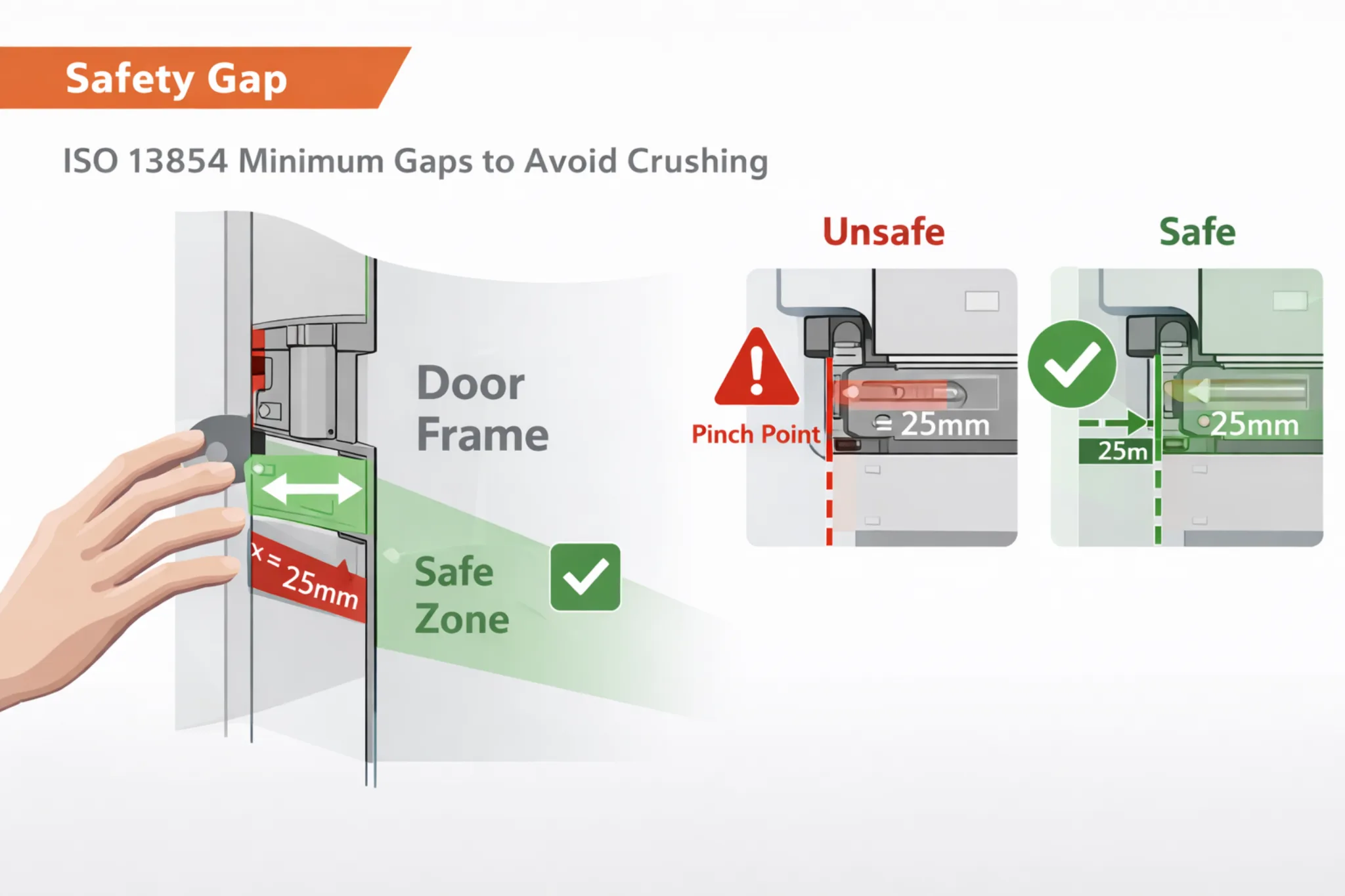
- Safety Gap: By limiting the range of motion of the door panel, the hinge stop helps maintain a safe gap between the door and the frame to a certain extent, preventing the door from crushing fingers during sudden closing.
- Multi-Stage Positioning: Many hinges with multi-position detents (such as the multi-stage opening positioners on car doors) provide stable dwell positions when the door opens, preventing pinch accidents caused by the door closing accidentally due to wind or gravity.
Stability Control (Preventing Center of Gravity Shifts)
Stop hinges constrain the opening angle, avoiding the instability risk of the equipment’s overall center of gravity shifting due to the lid opening too far.
- Tipping Risk: On large cabinets or equipment, if a heavy door opens past its limit, it likely causes an unsecured rack to tip forward.
- Solution: Using stop hinges to control the angle within a safe range ensures the center of gravity remains within the base support range. For example, designers restrict an industrial cabinet door to a half-open position to prevent the door’s weight from destabilizing the cabinet when fully open.
Maintaining Access Space
In narrow aisles or alongside crowded production lines, ensuring the door body does not protrude excessively is vital. The stop function prevents the door panel from obstructing personnel passage or sustaining accidental bumps from passersby.
In summary, the hinge’s stop function controls motion boundaries, eliminating or reducing operational risks such as pinching, tipping, and collisions from a mechanical essence, complying with the design safety principle of “risk minimization.”
Technical Details: Working Principles and Selection Matrix
Various technical solutions exist for implementing hinge stops. To assist engineers in making data-driven decisions, we have compiled the following selection matrix comparing the performance characteristics of different stop mechanisms.
| Mechanism Type | Load Capacity | Adjustability | Cycle Life (Est.) | Sealing Protection | Typical Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Cam/Gear | Low – Medium | Step / Infinite | 10k – 50k Cycles | Excellent (Sealed) | High |
| External Rods | Very High | Adjustable Length | 100k+ Cycles | Medium (Exposed) | Low – Medium |
| Internal Stamped Stop | Low | Fixed Only | 5k – 20k Cycles | Good | Low |
| Hydraulic Soft Stop | Medium | Fixed Range | 50k+ Cycles | Excellent | Very High |
Table 1: Comparative Analysis of Hinge Stop Mechanisms based on industrial engineering standards.
Internal Stops vs. External Stops
- Internal Stops:
- Structure: The hinge integrates the stop structure internally (e.g., cams or gears between leaves).
- Pros: No exposed parts, compact structure, simple installation, clean aesthetics.
- Cons: Limited by size, offers limited impact load capacity, and the angle usually lacks adjustability.
- Applicability: Small equipment pursuing a clean appearance.
- External Stops:
- Structure: Connects the door panel and the frame through independent rods, cables, or support arms. A door check typically acts as an independent metal rod to support and prevent the door from opening too wide.
- Pros: High structural strength, suits large heavy-duty doors/lids; allows convenient replacement or adjustment (by changing rod length).
- Cons: Requires extra installation space, exposed parts may affect aesthetics, requires regular inspection for loosening or corrosion.
- Applicability: Super heavy-duty applications like machine tool guard doors and large hatch covers.
Fixed Angle vs. Adjustable Angle
- Fixed Angle: Engineers define a single maximum opening angle (e.g., 90°, 110°) during design. The structure is simple and reliable, suitable for mass-produced standardized products.
- Adjustable Angle:
- Slot Stop: Manufacturers cut multiple fixed slots into the hinge arm, locking different angles by changing the position of the insert pin.
- Gear Meshing: Utilizes the relative rotation of paired gears to achieve infinite adjustment, fixed with a positioning pin.
- Hydraulic Damping: Built-in hydraulic dampers allow movement within a certain range and lock at the end point.
- Advantage: You can set opening angles as needed from 0° to 180° (or even 360°), greatly improving scenario adaptability.
Soft Stop vs. Hard Stop
- Hard Stop: Rigid components block the door panel directly. Positioning is accurate, but the impact force is high, potentially generating noise and vibration.
- Soft Stop: Elastic elements or damping mechanisms decelerate the door body gradually as it approaches the limit.
- Case: A stop hinge with hydraulic damping automatically buffers near the limit angle, protecting connections and reducing noise.
- Selection: Choose soft stops for occasions requiring silence (medical/high-end cabinets); choose hard stops for heavy equipment requiring pure mechanical strength.
Industry Application Analysis
Medical Equipment
Medical instruments extensively use hinges with stops to ensure operational safety.
- Observation Windows/Lids: Usually feature limit controls to ensure operators can safely view the interior without interfering with equipment operation, while avoiding collisions with nearby components.
- Mobile Carts: On medical cart doors or X-ray machine covers, the stop function prevents opening too violently and injuring medical staff, while supporting stability for single-handed operation.
Industrial Enclosures
In factory automation, stop functionality relates directly to maintenance efficiency and safety.
- CNC Machine Tools: Maintenance door designs often utilize stop hinges to limit the door body to a 120° opening, preventing interference with equipment operation.
- Power Distribution Cabinets: Designs often stop the door automatically after opening to a certain angle (half-open state), facilitating inspection while avoiding the cabinet door completely blocking the walkway.
Automotive Industry
The Door Check stands as a mandatory safety specification.
- Function: Provides multi-stage stops, preventing the door from suddenly opening fully or slamming shut on slopes or in high winds.
- Compliance: Meets ISO 13854 anti-pinch gap requirements, preventing the door’s leading edge from getting too close to the fender.
- Risk: Actual testing indicates that if the limiter fails due to fatigue, the door may shake or even open while driving; insufficient performance also leads to sagging, noise, and poor sealing.
Aerospace
- Cabin Facilities: Overhead bin doors use multi-link hinges combined with dampers to achieve a soft stop, preventing sudden dropping.
- Vibration Resistance: Especially in environments with swaying (like ships or aircraft), stop devices prevent hatches from closing on their own due to hull movement.
- Ground Equipment: Jet bridge guardrail doors and air cargo container doors feature limit rods to ensure they remain fixed in a safe position after opening.
Engineering Selection Guide: Calculation & Types
Correctly selecting a stop hinge requires determining not just the static load, but the dynamic impact potential. Below is a simplified engineering guide to ensure safety margins.
Load Calculation Model
When selecting a hinge for a “Safety Stop,” do not rely solely on the door weight. You must account for the Dynamic Impact Force generated when a door is flung open to its limit.
Selection Formula (Simplified):
$$ T_{rated} \ge (W \times D_{cog} \times SF_{dynamic}) $$
- $$T_{rated}$$: The hinge’s rated Max Stop Torque (Nm).
- $$W$$: Weight of the door (N).
- $$D_{cog}$$: Distance from hinge axis to the Center of Gravity (m).
- $$SF_{dynamic}$$: Dynamic Safety Factor.
- Gentle manual operation: 1.2 – 1.5
- Frequent/Fast operation: 2.0 – 3.0
Built-in Stop Hinges
- Applicable Scenarios: Lighter doors, compact space, need for good sealing, high requirements for appearance (e.g., medical device casings).
- Engineering Note:
- For super heavy-duty doors, the limit of the hinge itself may not suffer.
- We recommend reserving more than 20% margin on the hinge’s rated load capacity. Rationale: This buffer specifically accounts for the kinetic energy spike (impulse) that occurs at the exact moment of the mechanical stop, preventing instantaneous shear failure of the internal pins.
External Check Straps/Lanyards
- Applicable Scenarios: Large hoods, hatches, heavy machine tool maintenance doors (requiring large opening angles and heavy weights).
- Engineering Note:
- High design flexibility; you can freely choose rod length.
- Requires regular maintenance to check if connecting bolts and hinges are loose and if lubrication is good.
Expert Advice: If high aesthetics are required, prioritize reinforced internal stop hinges; if the load is extreme and space is ample, external limit rods serve as the more reliable option.
FAQ
Q1: Can I retrofit stop functionality to existing equipment?
A: Generally, yes. For doors or lids already in use but lacking limit protection, you can add external limit components.
- Solution: Many cabinet hinge manufacturers provide extra limit accessories. Taking a certain HTAN hinge model as an example, you can conveniently insert its restrictor accessory into the hinge cup before or after cabinet door installation to achieve retrofit needs.
- Note: For super-large door bodies, we recommend evaluating the addition of support rods or limit chains.
Q2: How much weight and frequency can a stop hinge withstand?
A: Premium hinges feature designs with sufficient margin.
- Data Reference: A heavy-duty hinge adopts double-gear meshing to enhance stop stability. Its wear-resistant bushings are validated through durability cycle testing benchmarked to recognized hinge standards (e.g., ANSI/BHMA A156.1 / EN 1935), and detailed results are available upon request.
- Corrosion Resistance: For outdoor applications, ensure the product meets ASTM B117 (Salt Spray Test) for at least 96 hours to prevent structural weakening of the stop mechanism due to rust.
- Selection Principle: You must select the corresponding grade based on the door weight and frequency, preserving at least a 20% load margin.
Q3: What causes noise in the stop mechanism?
A: Common causes include poor lubrication and part wear.
- Lubrication: Dry friction of metal parts leads to squeaking sounds (e.g., car door checks lacking oil after a year or two); adding appropriate grease can alleviate this.
- Wear: After long-term high-intensity use, pins and slots may become loose.
- Suggestion: Selecting stop hinges with damping can minimize noise.
Conclusion
The stop function, as a safety detail in hinge design, plays a significant role in improving the safety and quality perception of industrial equipment and various electromechanical products.
This design philosophy aligns with the principle in international standards like ISO 12100 to “prioritize risk reduction through inherent safe design.”
- Protecting Equipment: Prevents structural collisions, protects seals.
- Protecting Personnel: Eliminates pinching and impact hazards.
- Enhancing Quality: The solid feel and quiet effect brought by soft stops increase user confidence.
Incorporating hinge stops into consideration early in product development allows for a better balance of safety versus function, and cost versus aesthetics. This has become an important standard configuration for measuring the engineering reliability of industrial products.
Disclaimer: The engineering formulas and selection guides provided in this article are for general reference purposes only and do not constitute professional engineering certification. Actual product selection should be verified by professional engineers based on specific application environments, load conditions, and safety requirements.