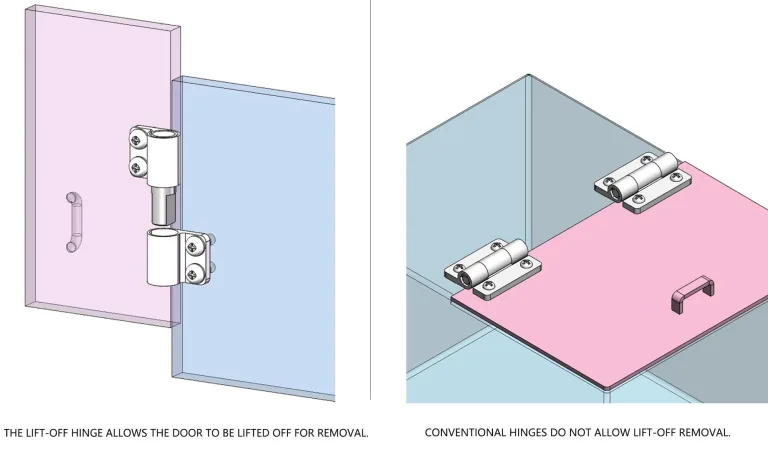
Why Torque Hinges Matter in Medical and Industrial Equipment
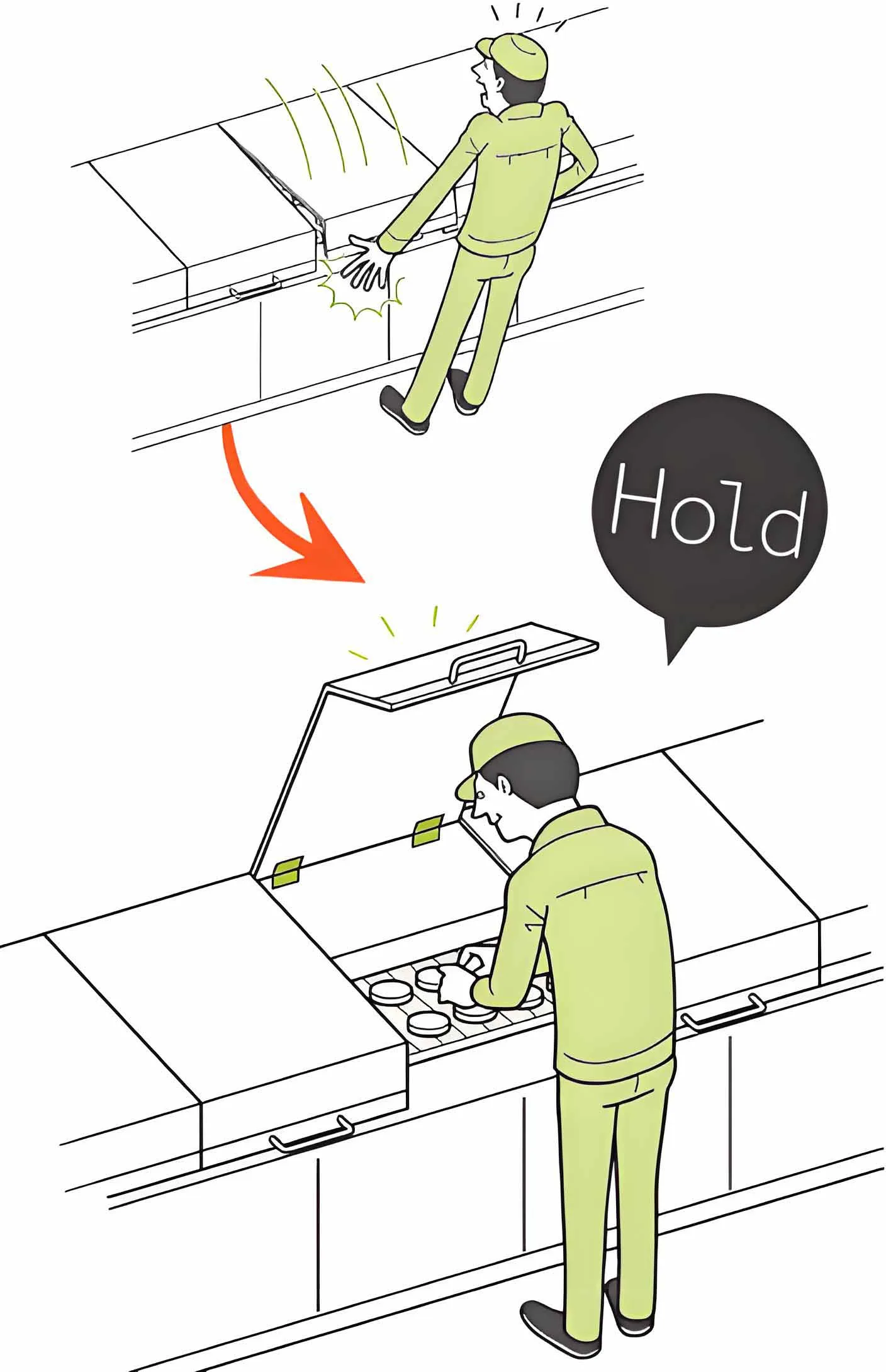
With torque hinges, machinery access doors won’t suddenly swing shut. Image source:sugatsune
Modern torque hinges solve a critical problem: they hold heavy lids, panels, or displays at any chosen angle without dropping or slamming. These hinges use internal friction or springs to provide a controlled resisting torque.
👉 In practice:
- A monitor arm stays in place once adjusted.
- A machinery access panel won’t suddenly swing shut.
Torque hinges are built for reliability, resisting wear and typically requiring no frequent maintenance — making them ideal for hospitals and factories.
What Is a Torque Hinge?
A torque hinge (also called a friction hinge or position-control hinge) is a mechanical hinge that uses internal friction or springs to resist rotation.
🔑 Key difference vs. normal hinges:
- Normal hinge: swings freely, no holding force.
- Torque hinge: provides a steady opposing force so panels and lids stay at any set angle.
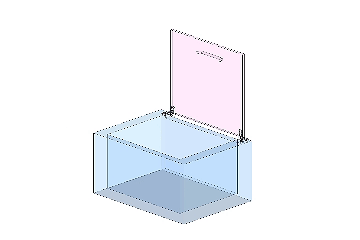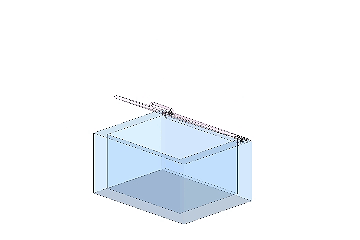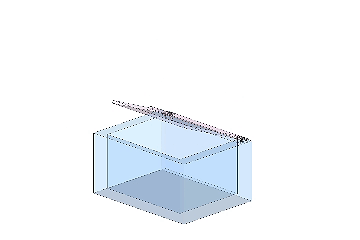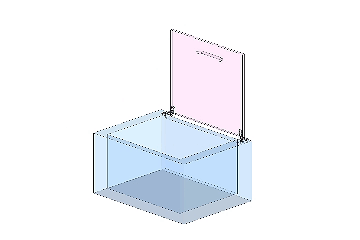
A cover with a torque hinge can stop and hold at any position
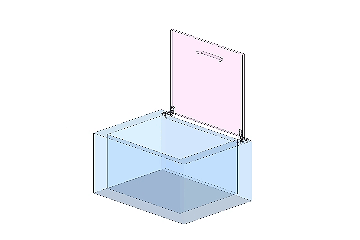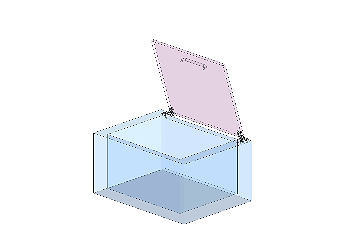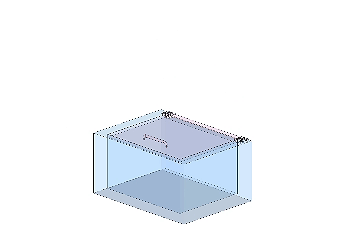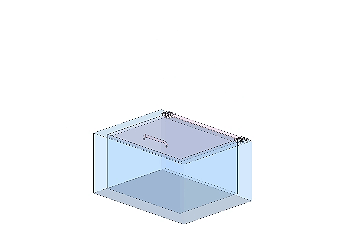
A cover with a standard hinge cannot stop at any position
📌 Example applications:
- Laptop screens (small torque hinges).
- Industrial/medical equipment (larger torque hinges for monitors, covers, or doors).
HTAN: Torque hinges are “suitable for holding lids, doors, panels or display devices at specific angles for extended periods.”(Reference: Lab Lid Slam: Safety Hazards & The Critical Role of Constant Torque Hinges)
How Torque Hinges Work
Inside a torque hinge:
- Springs, friction plates, or damping elements generate resisting torque.
- When the panel tries to move, the hinge pushes back with steady force.
📊 Torque requirement formula:
Torque ≈ (Weight × Distance) / 2- Weight: panel weight
- Distance: horizontal distance from hinge axis to panel’s center of gravity
👉 Always choose a hinge with resistive torque > panel torque (with safety margin).
Torque Ratings in Practice
- Common Units: N·m (SI) or kgf·cm (metric).
- Manufacturer ranges: HTAN offers from 0.006 N·m (58 gf·cm) up to 7 N·m (70 kgf·cm) depending on size.
📌 For heavy or large panels → use multiple hinges to share torque load.
Key Types of Torque Hinges

One-Way (Unidirectional) Torque Hinge
- Generates resistance in only one direction.
- Example: Lid opens easily, but resists closing to prevent slamming.

Bi-Directional Torque Hinge
- Provides torque in both opening and closing directions.
- Holds flap at any angle between 0°–180°.

Position-Control (Constant-Torque) Hinge
- Provides uniform torque across its range.
- Eliminates need for gas struts or lid stays.
- Common in medical monitors, diagnostic equipment.

Compact (Low-Profile) Torque Hinge
- Designed for space-constrained applications.
- Example: HTAN XG11-075 hinge — embedded, concealed, press-fit.
Core Performance Metrics
When evaluating torque hinges, engineers look at:
orque Rating
- Must meet/exceed panel torque.
- Specified in N·m or kgf·cm.
Cycle Life (Durability)
- Standard torque hinges: 10,000–25,000 cycles.
- Premium models: 50,000+ cycles.
- Example: HTAN tested hinges at 40,000 cycles; Southco’s ST-7A2 offers 2× cycle life vs older models.
Load Capacity & Angular Range
- Typically up to 180° swing.
- Heavy panels require multiple hinges.
- Specialized models allow multi-axis motion.
Applications in Medical Devices
Medical devices demand precision, stability, and hygiene.
Benefits of Torque Hinges:
- Precision & Stability: Imaging monitors and surgical lights stay at exact positions.
- Safety: Prevents sudden drops/slams.
- Cleanability: Stainless steel & sealed hinges resist corrosion and cleaning agents.
Common Medical Applications:
- Display Monitors & Touch Screens
- Surgical Lighting (multi-joint, no drift)
- Medical Carts & Cabinets (hands-free lids)
- Diagnostic Equipment Covers
Applications in Industrial Equipment
Industrial use requires robust and durable hinges.
Challenges Solved:
- Vibration resistance
- Harsh environments (chemicals, dust, temperature extremes)
- Heavy-duty loads
Common Industrial Applications:
- Control Panels & Access Doors
- Protective Machinery Covers
- Vehicle Consoles & Heavy Equipment Panels
Comparison: Torque Hinges vs. Alternatives
| Feature | Ordinary Hinge | Gas Spring/Strut | Torque Hinge (Friction) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position Holding | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (open only) | ✅ Yes – any angle |
| Space Requirement | ✅ Minimal | ❌ High | ✅ Low (compact) |
| Maintenance | ✅ Low | ❌ Moderate (leaks) | ✅ Very low (sealed) |
| Cycle Life | Variable | Medium | ✅ High (20k–100k+) |
| Cost & Complexity | ✅ Low | Moderate–High | Moderate (precision) |
How to Choose the Right Torque Hinge
- Calculate Required Torque
- Use formula: (Weight × Distance)/2
- Add 25–50% safety margin
- Check Parameters
- Torque Range (fixed or adjustable)
- Cycle Life (choose ≥ expected product lifetime)
- Material (stainless steel, anodized aluminum)
- Environment (chemicals, moisture, outdoor)
- Mounting (surface, embedded, flush)
- Brands & Certifications
- Trusted brands: Southco, HTAN, Reell, TorqMaster
- Look for ISO 9001, RoHS/REACH compliance, FDA-approved materials
Future Trends in Torque Hinges
- Smart Hinges: Built-in sensors for angle/load reporting, predictive maintenance.
- Advanced Materials: Lightweight composites, PVD coatings, polymer friction elements.
- Additive Manufacturing: Custom-designed hinge internals for robotics and medical devices.
FAQ
- Difference vs normal hinge? Normal = free swing, Torque = position holding.
- Does my device need torque hinges? Yes, if it has adjustable lids/screens that must stay in place.
- Replacement cycle? Standard 10k–25k cycles; premium 50k+.
- Maintenance required? Usually maintenance-free. Replace when resistance drops.
- Does brand matter? Yes. Choose certified manufacturers (Southco, HTAN, Reell).
Conclusion
Torque hinges are mission-critical for both medical and industrial applications:
✅ Safety: Prevent accidents, drops, and slams.
✅ Efficiency: Hold equipment at any position smoothly.
✅ Durability: Withstand tens of thousands of cycles.
✅ Space-Saving: Replace bulky struts/rods.
As IoT and automation expand, torque hinges will evolve further — becoming smarter, lighter, and more durable, ensuring they remain indispensable in critical equipment design.