Why Torque Hinges Outperform Standard Hinges in Durabilit
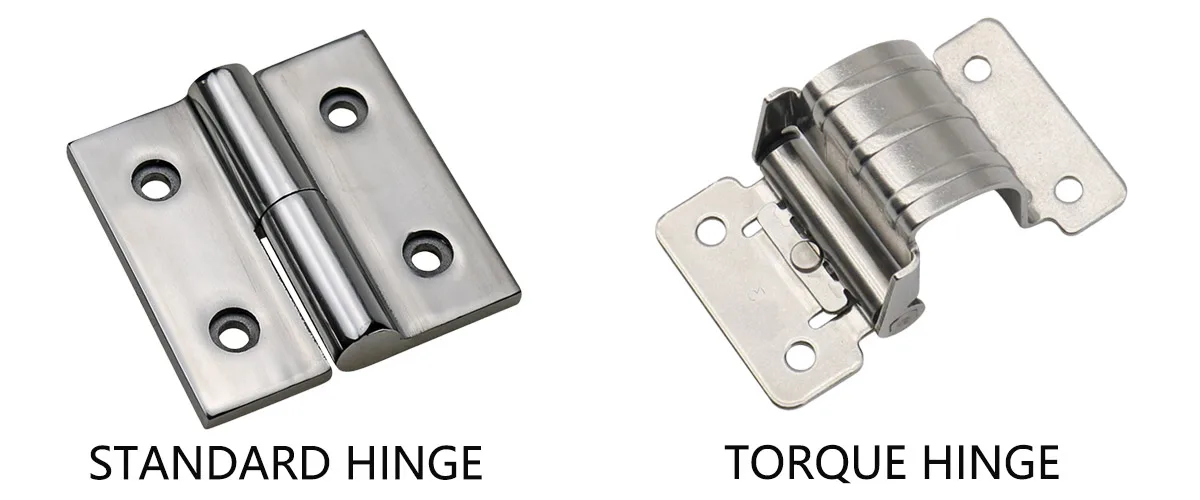
Standard Hinge vs. Torque (Friction) Hinge
Products with moving parts—from laptop screens to medical displays to vehicle dashboards—rely on hinges for smooth operation and safety. Conventional hinges often fail due to wear, loosening, and environmental stresses. Over time:
- Worn hinge pins
- Loosened screws
- Absence of built-in resistance
…can cause panels to slam shut or sag on their own, degrading user experience and increasing damage risk.
In contrast, torque (friction) hinges utilize an internal friction mechanism to generate “resistance” within the pivot, counterbalancing panel torque and enabling panels to hold at any angle.
The Role of Hinges in Modern Products
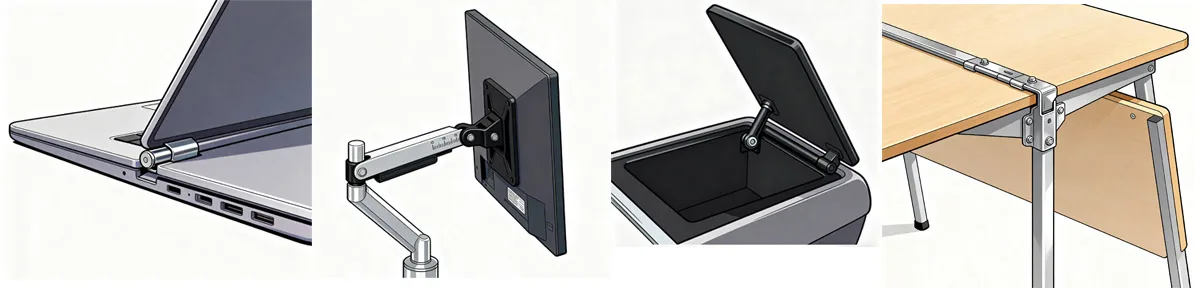
Hinge Applications in Different Products (Laptops, Medical Displays, Automotive Consoles, Office Furniture)
Hinges have evolved far beyond simple door joints into precision components. Today, everything from aircraft interiors to office furniture relies on specialized hinges for durability and comfort.
Categories of hinges:
| Functional Category | Type | Features & Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Closing | Spring Hinge | Built-in spring, allows the door to close automatically; common in cabinet doors and small doors. |
| Self-Closing Hinge | Automatically pulls the door shut after opening; often used in wooden doors and office furniture. | |
| Soft-Close / Silent | Soft-Close (Damping) Hinge | Integrated hydraulic or damping system, slows down door closing to avoid slamming; widely used in premium cabinets and wardrobes. |
| Positioning / Holding | Torque (Friction) Hinge | Uses friction to hold doors/screens at any angle; common in laptops, medical devices, automotive displays. |
| Multi-Position Hinge | Designed to stay fixed at specific angles (e.g., 30°, 90°, 135°); suitable for flip covers or display cases. | |
| Special Opening | Lift-Up / Drop-Down Hinge | Allows upward or downward door opening; often used in overhead cabinets and showcases. |
| Folding Hinge | Enables bi-fold or collapsible furniture doors. | |
| Angle Hinge | Provides extended opening angles (30°, 45°, 135°, 165°); suitable for corner cabinets or complex structures. | |
| Heavy-Duty & Adjustable | Adjustable (Lift) Hinge | Allows vertical adjustment of the door; useful for precise cabinet alignment. |
| Heavy-Duty Hinge | Designed for heavy doors or panels; high load-bearing capacity, used in metal gates and large enclosures. |
Impact of hinge design:
- Smooth operation
- Load capacity
- Safety
- Aesthetics (torque hinges often “disappear” within products)
Example: Laptop displays exemplify friction hinges—screens hold at any angle without wobbling.
Why Ordinary Hinges Fail
Mechanical Weaknesses
- Lack of built-in braking/resistance
- Wear at pivot pins and blades
- Vibration loosens screws, creating gaps
- Heavy panels drop or sag under own weight
- Long-term metal-on-metal friction accelerates wear
Design Limitations
- Only enable rotation, no locking at intermediate angles
- Require limiters or gas springs to hold position
- Load concentrated at hinge joint → premature damage
Example:
A heavy cabinet door supported by only two hinges → entire weight stresses small hinge joint + screws.
Comparison:
- Standard hinges: Swing freely, require external stops
- Torque hinges: Provide counter-torque, hold panels at any angle
Environmental Factors
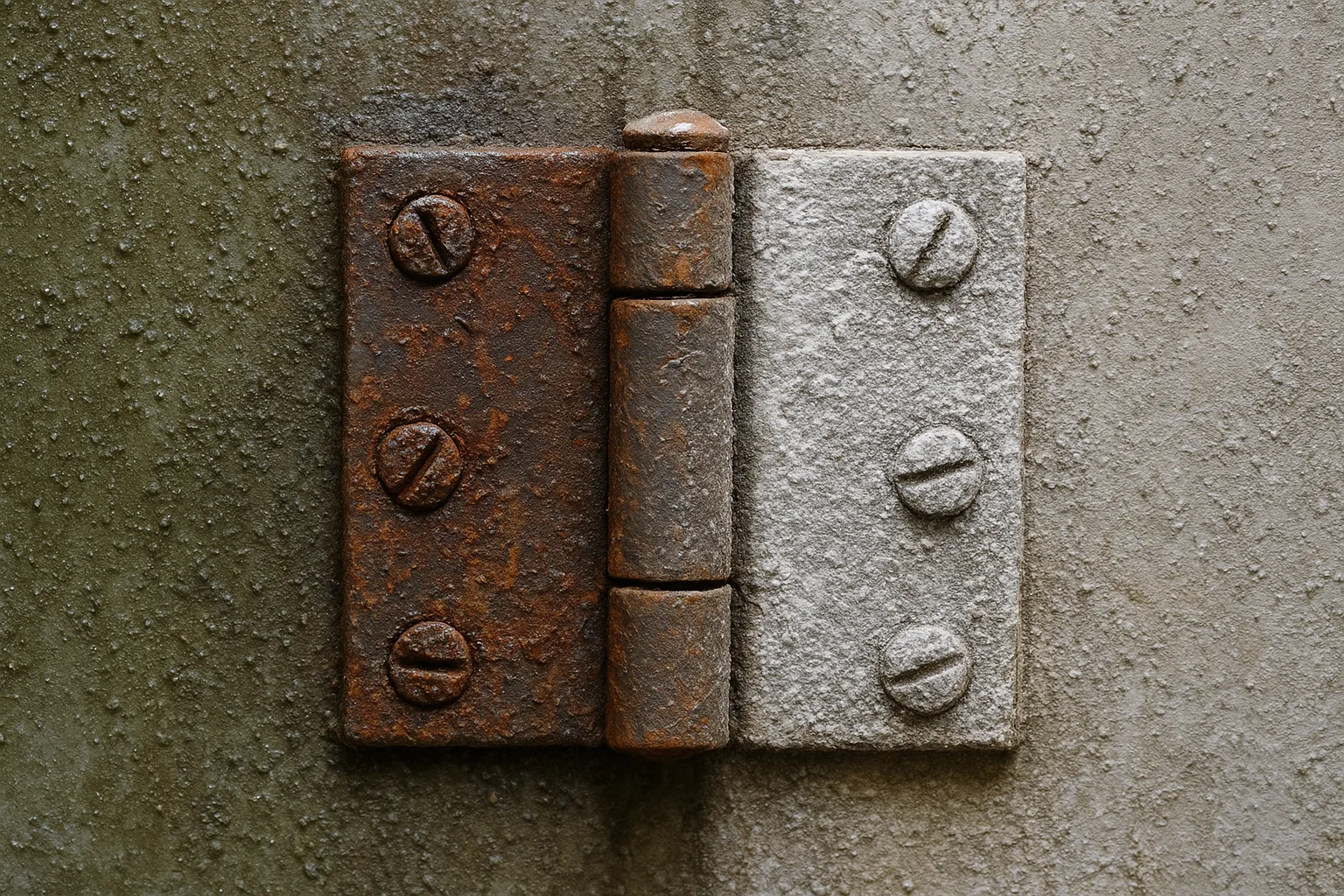

Impact of Harsh Environments on Standard Hinges
Standard hinges degrade under:
- Dust
- Humidity
- Salt spray〔consult:ASTM B117〕
- Extreme temperatures
Issues:
- Moisture → corrosion
- Dust → accelerated wear
- Temperature cycles → lubricant dry-out, clearance increase
- Severe cases → seize or deform
Durability Comparison:
| Hinge Type | Typical Cycle Life | Environmental Protection | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard consumer hinge | Short lifespan | Poor | Often loosens, corrodes |
| Concealed door hinge (ISO standard) | ~200,000 cycles | Moderate | Meets ISO test |
| Premium torque hinge | 20,000–100,000 cycles | IP65–IP68 | Torque decay <15% |
The Rise and Solution of Torque Hinges
What is a Torque (Friction) Hinge?
- Generates consistent resistance during movement
- Uses friction pads, springs, or dampers
- Absorbs energy → prevents abrupt movements
- Holds cover at any angle without limiters
Key Features of Torque Hinges
- Stepless Positioning: Any angle, no latches/stops
- Adjustable/Fixed Torque: Preset or adjustable via screws/preload
- High Load Capacity: Up to 500 N·m+
- Smooth Controlled Motion: Damped, noise-free
- Long Service Life: 100,000+ cycles, torque decay <15%
- Customizable: Materials, shape, mounting, finish
How Torque Hinges Solve Conventional Hinge Issues
- Prevents unintended movement (no self-closing/swinging)
- Eliminates extra supports (no gas springs/rods)
- Smoother & safer (anti-impact, anti-pinch)
- Low maintenance (lubrication-free, stable)
- Enhanced UX (professional-grade feel, stable positioning)
Torque Hinge Applications
- Consumer electronics: Laptops, foldable phones, displays, camera screens
- Automotive/transportation: Dashboards, glove boxes, aircraft trays
- Medical equipment: Surgical lights, monitor mounts, hospital beds
- Furniture & industrial: Adjustable desks, lift-up doors, CNC panels
Torque Hinge Advantages
- Enhanced Reliability & Safety
- Superior User Experience
- Increased Durability & Cost Savings
- Design Flexibility
Key Selection Factors
- Load capacity & torque requirement
- Material & surface finish
- Environmental rating (IP, corrosion, temperature)
- Mounting method & dimensions
- Certifications (ISO, UL, RoHS)
Real-world Applications
- Laptops: Stable screens at any angle
- Industrial cabinets: Secure heavy steel doors
- Medical equipment: Precision monitor mounts
- Furniture: Flip-top tables, smooth & quiet
Common Misconceptions
❌ Only for high-end equipment → False
❌ Too expensive → Long-term cost savings
❌ Hard to adjust/maintain → Mostly maintenance-free
❌ Will wear out quickly → Often outlasts product life
Future Trends
- Smart hinges: Sensor-equipped (angle + usage data)
- New materials: Composites, carbon fiber
- Sustainability: Recyclable + eco-coatings
- 3D printing: Custom geometries
- Stricter standards: High-cycle UL/ISO certifications
Conclusion
Standard hinges = weak point → loosen, wear, fail.
Torque hinges = stable positioning + resistance → enhance safety, durability, and UX.
FAQ
Q: Why do standard hinges fail easily?
A: Pin wear, screw loosening, corrosion, lack of resistance → sagging/slamming.
Q: What distinguishes them from torque hinges?
A: Torque hinges = rotational resistance → hold any angle. Standard hinges = swing freely.
Q: Where are torque hinges used?
A: Laptops, phones, vehicles, planes, medical, industrial, furniture.
Q: Lifespan?
A: 100,000+ cycles, minimal torque decay.
Q: Cost?
A: Higher upfront, but replaces multiple parts, longer life = cheaper overall.
Q: Customizable?
A: Yes → torque, material, finish, mounting, design flexibility.
This article was prepared by the HTAN engineering team, specializing in hinge design and manufacturing with 10+ years of experience in consumer electronics, medical equipment, and industrial applications.