Industrial Lift-Off Hinges: Complete Guide to Design and Use
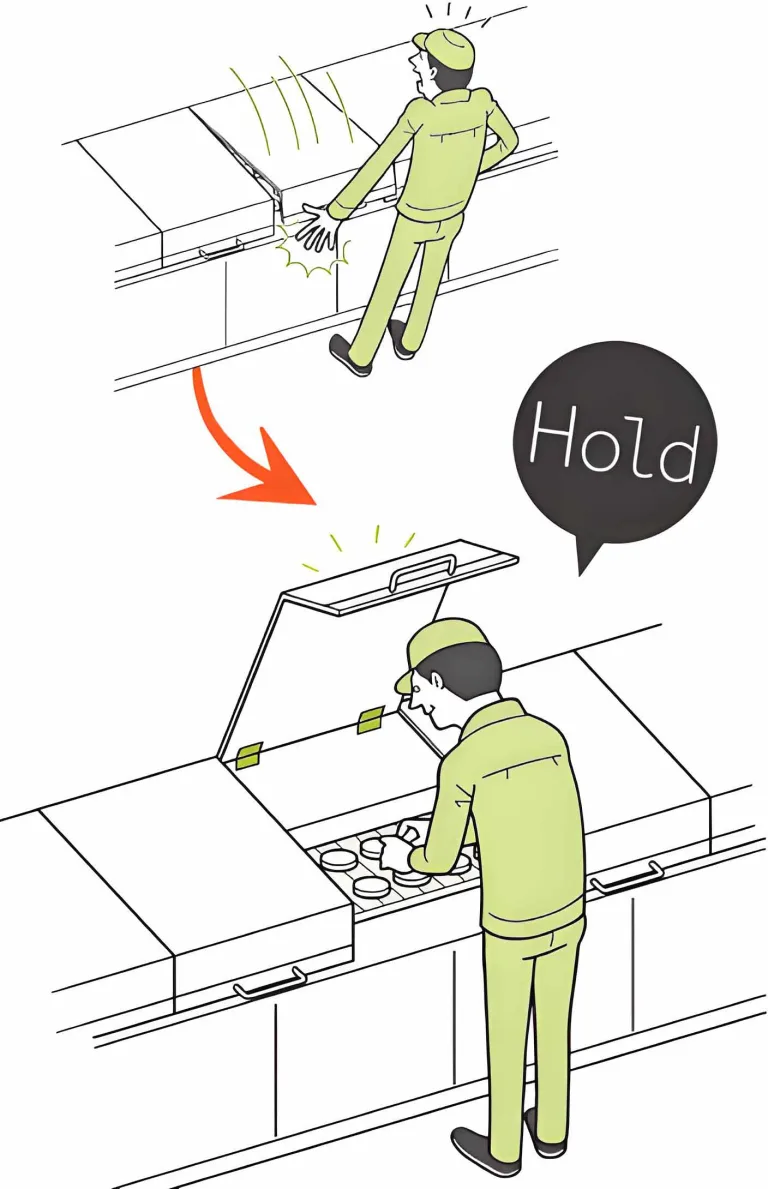
In modern industrial settings, technicians frequently need to quickly detach door panels from electrical control cabinets, enclosures, or equipment housings for maintenance or repairs.
The Lift-Off Hinge is specifically engineered for this purpose, allowing door panels to separate from their frames through a “vertical lift-off” motion—without the need for screws or tools. This design greatly improves disassembly efficiency and precision. For a detailed explanation of the definition and operating principles of Lift-Off Hinges, refer to the Introduction section.
Technicians simply lift the door panel slightly to detach it from the frame—allowing removal within seconds. This reduces maintenance time and operational complexity compared to traditional hinges.
What is a Lift-Off Hinge?
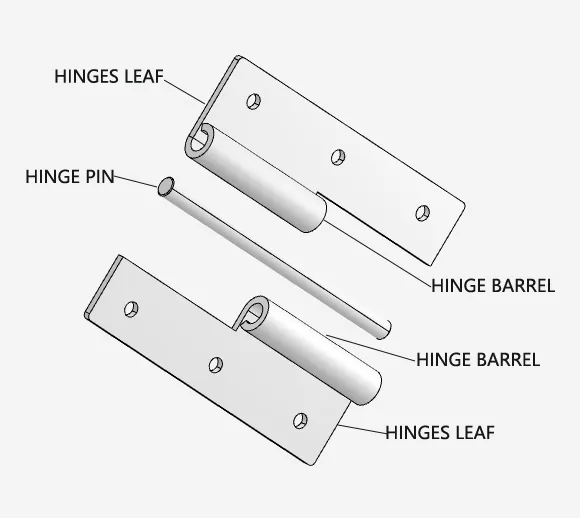
Diagram of a Lift-Off Hinge showing the hinge leaf, hinge pin, and hinge barrel.
A lift-off hinge is a specialized hinge structure typically composed of two hinge leaves: one mounted on the door frame with a fixed pin, and the other attached to the door panel, forming a hollow hinge barrel.
During installation, the two leaves connect via the pin to create a pivotable structure. Unlike standard double-leaf hinges, the lift-off hinge allows the door panel to detach from the pin when lifted vertically, enabling easy separation.
In other words, one leaf remains fixed to the frame while the other stays attached to the door. When the door panel is lifted upward, the two leaves automatically separate, facilitating quick removal.
This feature sometimes earns them the names “detachable hinges” or “pin-release hinges,” as they simplify routine maintenance without requiring additional tools.
Core components include:
- Hinge leaves: One mounted on the door frame, one on the door panel.
- Pin: Permanently fixed to the frame-side leaf, providing the pivot point.
- Hinge eye: A hollow opening formed in the door leaf’s hinge plate that engages with the pin.
Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum alloy, and carbon steel.
Corrosion resistance can be enhanced through galvanization, powder coating, or electroplating.
For example:
- Stainless steel suits highly corrosive environments.
- Aluminum alloy offers lightweight rust resistance.
- Carbon steel offers superior strength for heavy-duty applications.
Lift-off hinges are further categorized by opening direction into left-opening and right-opening types:
Standing outside the door facing the hinge side, if the hinge is on the left side of the door, select the left-opening type; conversely, select the right-opening type.
Working Principle
Rotational Movement:
The door panel is connected to the door frame via a pin shaft fixed on the frame side, allowing it to open and close like a standard hinge. Two sets of hinges—upper and lower—jointly support the door’s weight, enabling it to rotate around the pin for opening.
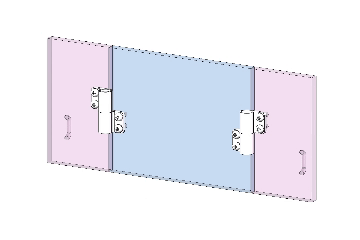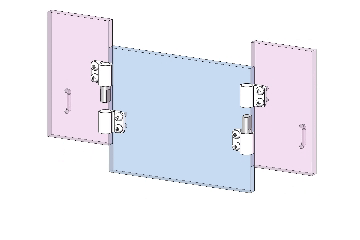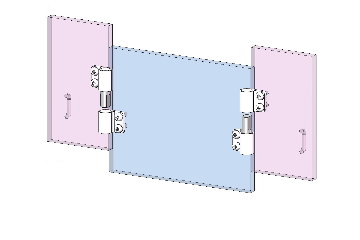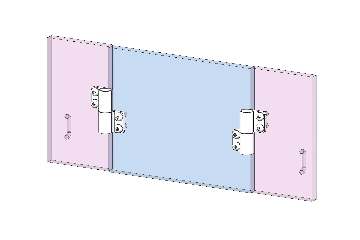
Vertical lift-off motion showing door removal without tools.
Lift-and-Separate:
To remove the door panel, simply lift the door vertically upward. This disengages the hinge pin on the door panel from the pin in the frame hinge, causing the door panel to separate automatically. This “tool-free” mechanism greatly simplifies disassembly.
Gravity Alignment:
When the door panel descends and aligns with the pivot pin, gravity automatically positions it. The pin re-enters the hinge pin hole to complete the connection, ensuring precise realignment upon door closure.
Safety Mechanism:
Some lift-off hinges incorporate groove-locking or positioning pin structures to prevent accidental door slippage. For instance, when the door is unsecured, the positioning pin limits the door’s lifting height, enhancing operational safety.
This structural synergy allows lift-off hinges to perform like standard hinges during operation while enabling quick panel removal through a simple lifting motion. Learn more about how Lift-Off Hinges work and their component design
in the Introduction section
The key feature of a removable hinge is the interaction between the pin and hinge barrel: doors open and close normally during use, while maintenance requires only lifting the door panel for tool-free disassembly.
Comparison of Lift-off hinges vs. Traditional Hinges
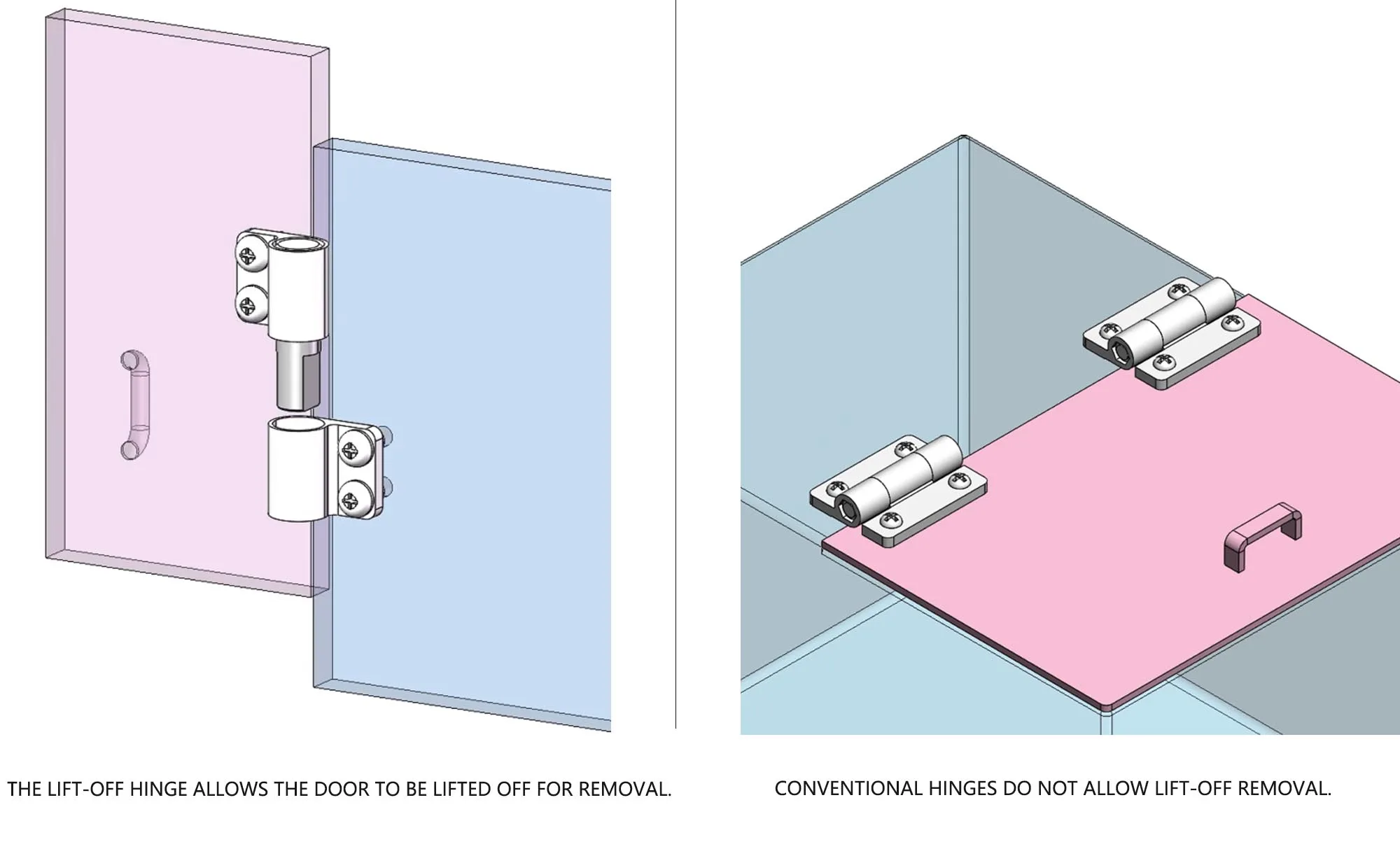
Structural and functional comparison between Lift-Off and traditional hinges
Lift-off hinges differ significantly from traditional hinges in structure and function. The table below summarizes their key distinctions:
| Feature | Detachable Hinge | Traditional Hinge |
|---|---|---|
| Removal Method | Vertical lift for separation, no tools required | Requires unscrewing bolts or removing pins to detach |
| Maintenance Efficiency | Quick maintenance operations, saving time | Time-consuming maintenance requiring tools |
| Installation Flexibility | Flexible assembly/disassembly, enabling rapid door panel replacement | Fixed installation, inconvenient to remove once installed |
| Suitable Applications | Industrial control cabinets, equipment enclosures, conveyor doors, and other scenarios requiring frequent disassembly | Household doors, light-duty structures, and other fixed-use scenarios |
| Cost | Slightly higher due to material and manufacturing complexity | Generally lower |
The comparison reveals that lift-off hinges offer significant advantages in maintenance efficiency and ease of use.
The removable hinge design allows technicians to quickly detach and reattach door panels (no extra tools required—simply lift the panel), drastically reducing downtime for repairs and cleaning. This is crucial for applications requiring frequent maintenance or component replacement.
Conversely, traditional hinges involve cumbersome disassembly processes—typically requiring screw removal or pin striking—resulting in lower efficiency.
Although lift-off hinges carry slightly higher costs, their enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime expenses often deliver greater value in industrial applications.
Design and Selection Considerations
When selecting detachable hinges, comprehensively evaluate the following factors:
Load Capacity Requirements:
Choose hinge load ratings based on door weight and dimensions. Heavy doors require multiple hinge sets for support and should use high-strength models. Hinge load classifications and endurance test procedures are defined in recognized standards, such as ANSI/BHMA A156.1and DIN EN 1935, which provide guidance on selecting hinges according to door mass, usage frequency, and durability requirements.
Material Selection:
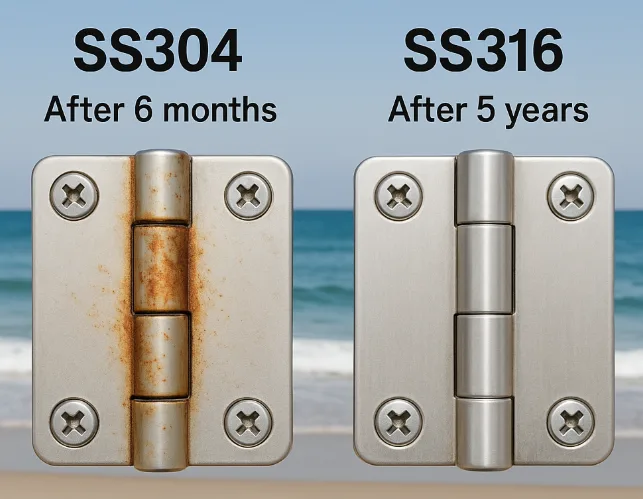
Environmental conditions dictate material choice. Stainless steel (e.g., 304 or 316 grades) is recommended for humid or chemically corrosive environments. Weight-sensitive or cost-critical applications may use aluminum alloy (anodized) for reduced weight. In standard industrial settings, carbon steel hinges offer high strength but require zinc plating or spray coating for rust prevention.
Door Opening Direction:
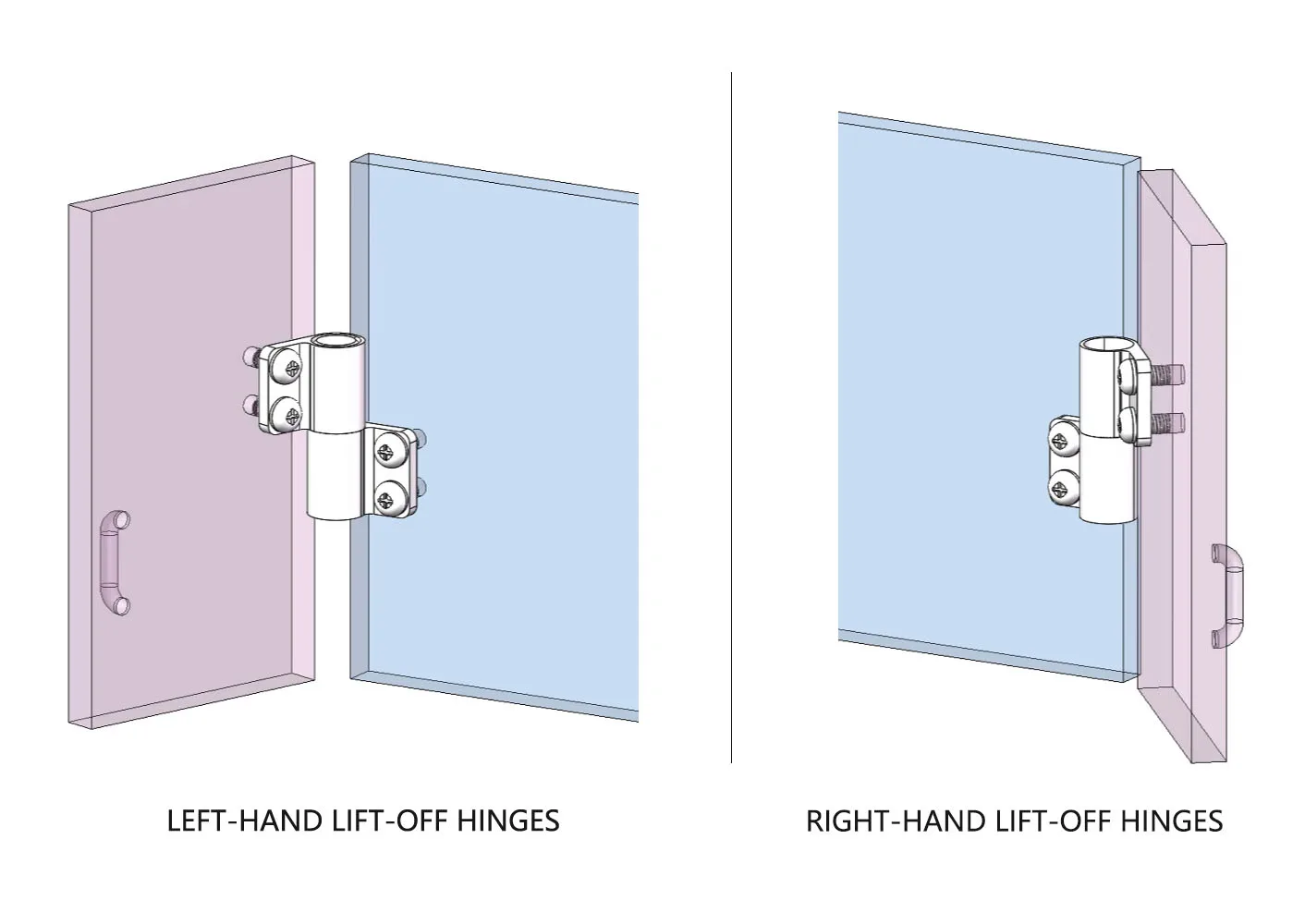
Determining left-hand and right-hand hinge orientation
Select left-hand or right-hand hinges based on the door’s opening direction. The general rule is: when standing outside the door, if the hinge is on the left side, it is a left-hand hinge; otherwise, it is a right-hand hinge. Always verify the opening direction during selection to ensure proper alignment after installation.
Installation Method:
Lift-off hinges typically offer welded or screw-mounted installation. Welded hinges are fixed to the frame via welding, commonly used for doors bearing heavier loads. Screw-mounted hinges use screws for fixation, offering easy installation and replacement.
Some hinges incorporate a pre-installed pin mechanism that allows quick door removal when needed. Selection should be based on cabinet structure and maintenance requirements.
Surface Treatment:
Surface treatments enhance hinge corrosion resistance. Common options include zinc plating, chrome plating, powder coating, and anodizing.
For instance, stainless steel hinges with zinc plating or powder coating are preferred for outdoor or chemical environments. Polished or chrome-plated finishes are suitable for laboratories or medical equipment, improving cleanability and aesthetics.
Maintenance Recommendations:
To ensure long-term reliable operation, regularly clean and lubricate hinge pins and moving parts. Remove dust and grime with a clean cloth, promptly addressing any rust spots. Apply a suitable lubricant (e.g., silicone or machine oil) to the pin surfaces to prevent rust and ensure smooth movement.
Replace hinges immediately if severe surface peeling or door sagging occurs.
In summary, when selecting hinges, decisively choose appropriate specifications by comprehensively evaluating door parameters, environmental conditions, and usage requirements to ensure compatibility with the application scenario.
Common Application Scenarios
Lift-off hinges offer efficient disassembly and high load capacity, making them widely applicable in the following scenarios:
Industrial Control Cabinets and Enclosures:
In electrical cabinets, distribution boxes, and automation equipment enclosures requiring frequent maintenance or component replacement, lift-off hinges enable rapid door panel removal, minimizing downtime for repairs.
Medical and Laboratory Equipment:
Medical devices, cleanroom equipment, or laboratory fume hoods require regular disinfection and deep cleaning. For these environments, components must comply with EHEDG or FDA hygienic design guidelines, ensuring both cleanability and corrosion resistance. Lift-off hinges facilitate door panel removal for thorough sterilization and component replacement, ensuring the integrity and cleanliness of sterile environments.
Transportation Equipment:
On trucks, containers, ship compartments, and heavy machinery where hinges bear door panel weight and require frequent disassembly for inspection. Lift-off hinges on cargo doors, hatch doors, etc., facilitate rapid replacement of damaged panels or maintenance checks.
Construction & Display Fixtures:
Examples include removable interior partition doors, display cabinet doors, or specialty furniture doors. Lift-off hinges enable sleek, minimalist designs while allowing temporary panel removal to widen passageways when moving large objects.
In these scenarios, convenience and reliability are the key advantages of lift-off hinges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do I determine whether to use left-opening or right-opening hinges?
A: Stand outside the door facing the hinge side. If the hinge is on the left side of the door, use left-opening hinges; if on the right side, use right-opening hinges. During installation, ensure the pin is on the door frame side, otherwise the door panel may not align correctly.
Q: Can lift-off hinges support heavy doors?
A: Yes. Various load-capacity lift-off hinges are available on the market. Select a hinge model rated for the door panel’s weight and use multiple hinges to distribute the load, ensuring suitability for heavy doors.
Q: Are lift-off hinges suitable for outdoor or humid environments?
A: Yes. We recommend corrosion-resistant stainless steel hinges (e.g., 316 stainless steel) or hinges with specialized anti-corrosion treatment. Note that 304 stainless steel may rust in high-humidity or salt-laden environments; for demanding marine or chemical settings, 316-grade material is preferred.
Q: Are any tools required to remove door panels?
A: No additional tools are required. The detachable hinge design allows technicians to lift the door panel directly, separating it from the hinge assembly. Ensure the door weight is properly supported during lifting to prevent the panel from falling and causing injury. For reinstallation, align the panel with the pin position and gently lower it into place.
Q: In which industries are lift-off hinges commonly used?
A: lift-off hinges are widely applied across multiple sectors, including electrical distribution cabinets, industrial automation equipment, medical devices, transportation vehicles, and telecommunications cabinets. Any equipment requiring frequent access, cleaning, or panel replacement benefits from the convenience of removable hinges.
Conclusion
Understanding the design principles and operational mechanisms of lift-off hinges helps engineers and technicians enhance equipment maintenance efficiency and user experience.
Through its innovative pin-axis structure, the removable hinge enables efficient, tool-free installation and removal while ensuring durability and versatility.
This design makes equipment maintenance more convenient and safer, meeting demands across diverse complex environments.
Designers should carefully consider door panel weight, environmental conditions, and operational requirements to fully leverage the advantages of lift-off hinges.
With an understanding of the design and functionality of lift-off hinges, engineers and procurement personnel can better select suitable hinge products to build efficient and reliable cabinet and equipment systems.