2026 Hinge Guide: Stainless Steel vs. Aluminum for Medical & Cold Chain

For engineers designing medical devices or cold chain transport units, the 2026 hardware specification is defined by a single trade-off: Durability versus Efficiency.
According to the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM) — a leading global authority on supply chain research and performance — downtime and critical hardware failures represent significant operational and financial risks for enterprises (see ASCM Research & Publications).
On one side, intensified FDA scrutiny on surface sanitation demands materials that can withstand harsh chemical washdowns without corroding. On the other, the rapid electrification of logistics fleets requires every component to shed weight to maximize vehicle range.
This creates a conflict in material selection. Should you choose the chemically resistant “armor” of AISI 316 Stainless Steel, or the lightweight versatility of 6061 Aluminum Alloy?
This guide cuts through the noise. We analyze these two materials based on strict ASTM standards to help you solve this engineering paradox.
The Core Battle: Deep Analysis of Physical Properties
Before discussing specific applications, we must understand the fundamental physical properties of these materials. The following data is based on ASTM A240 (Standard for Stainless Steel) and ASTM B209 (Standard for Aluminum Alloy).
Stainless Steel: The Benchmark for High Strength and Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel remains the top choice for heavy industry and environments requiring high sanitary standards. It is an iron-based alloy containing at least 10.5% chromium.
- AISI 304 (UNS S30400):
- This is the most common austenitic stainless steel.
- Characteristics: Offers good corrosion resistance and excellent formability.
- Limitations: In high-salinity environments (such as coastal areas), it is susceptible to Pitting Corrosion.
- AISI 316 (UNS S31600):
- Contains 2%-3% Molybdenum.
- Characteristics: The addition of molybdenum significantly improves resistance to Chlorides and industrial solvents.
- Applicability: Industry-standard for “Medical Grade” or “Marine Grade” applications.
- Physical Data:
- Density: Approx. 7.9 g/cm³ (0.29 lb/in³).
- Tensile Strength: Typically exceeds 515 MPa (75 ksi).
- Young’s Modulus: 193 GPa (28,000 ksi). This indicates high stiffness and resistance to deformation.
Aluminum Alloy: The Balance of Lightweight and Functionality
Aluminum alloys enhance pure aluminum by adding elements like magnesium and silicon to increase strength.
- 6061-T6 Aluminum Alloy:
- Contains magnesium and silicon.
- Characteristics: Excellent structural strength and toughness. It is the standard choice for general engineering applications.
- Surface Treatment: Must undergo Anodizing to prevent surface oxidation and blackening.
- 5052 Aluminum Alloy:
- The primary alloying element is magnesium.
- Characteristics: Exhibits superior corrosion resistance in marine atmospheres and higher fatigue strength than 6061.
- Physical Data:
- Density: Approx. 2.7 g/cm³ (0.098 lb/in³). Note: This is only one-third the weight of stainless steel.
- Tensile Strength: 6061-T6 is approx. 310 MPa (45 ksi).
- Young’s Modulus: 69 GPa (10,000 ksi). Its rigidity is about one-third that of steel, meaning it will experience more elastic deformation under heavy loads.
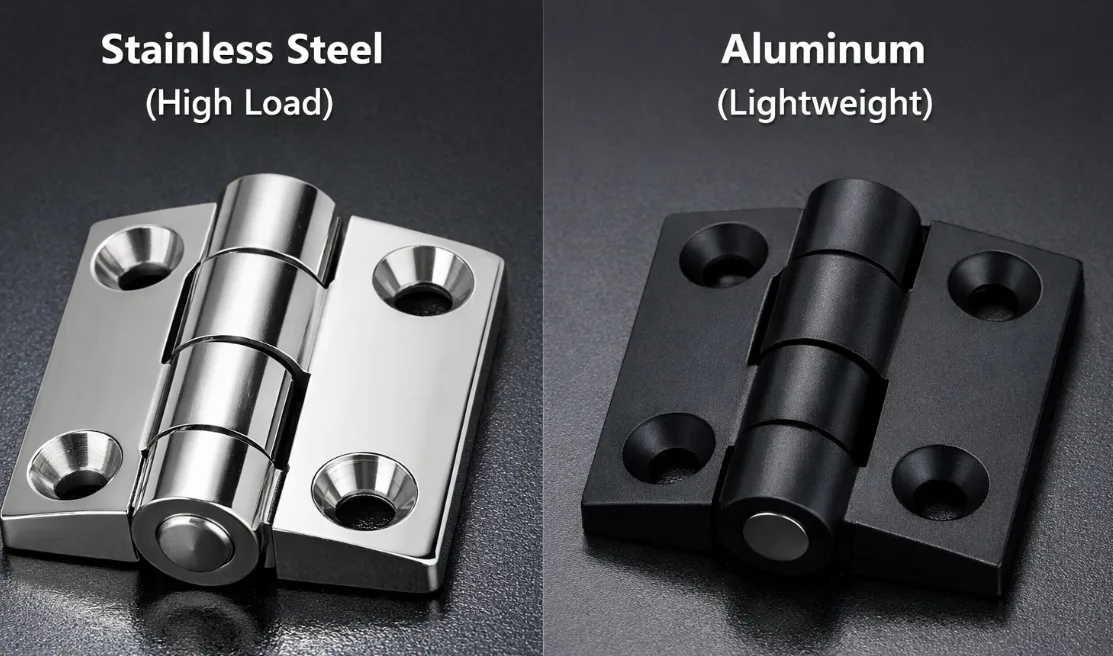

Selection Strategy for Medical Equipment
The medical environment imposes three core requirements on hardware: Sterility Control, Chemical Resistance, and Silent Operation.
Operating Rooms and Sterile Laboratories
- Recommended Material: Stainless Steel AISI 316 / 316L.
- Technical Rationale:
- Chemical Resistance: Hospitals daily use potent disinfectants, such as Quaternary Ammonium compounds and Bleach. High-pH alkaline cleaners can destroy the anodic layer of aluminum alloys. 316 Stainless Steel resists these chemicals effectively.
- Surface Finish: According to ISO 14644 Cleanroom Standards, surface roughness (Ra) should be below 0.8 microns. Polished stainless steel easily meets this standard, leaving no micropores for bacteria to colonize.
Mobile Medical Carts and Diagnostic Devices
- Recommended Material: Anodized Aluminum Alloy.
- Technical Rationale:
- Ergonomics: Nurses push medical carts several miles per day. Switching hinges and structural components from steel to aluminum can reduce total cart weight by 6-11 lbs (3-5 kg). This significantly reduces operator fatigue.
- Aesthetics and Identification: Anodizing processes compliant with MIL-A-8625 Type II standards allow for color coding (e.g., Red for Emergency carts, Blue for Anesthesia), aiding visual management in hospitals.
Special Case: MRI Rooms
- Critical Warning: Standard 304/316 stainless steel can retain weak magnetic properties after cold working.
- Solution: For MRI environments, engineers must specify “Fully Austenitic” stainless steel. Alternatively, utilize Aluminum or Titanium alloys, as aluminum is a Paramagnetic material and will not interfere with the MRI magnetic field.
Selection Strategy for Cold Chain Logistics
As of late 2025, the US cold chain logistics market is undergoing a massive technical upgrade. Under the ATP Agreement (Agreement on the International Carriage of Perishable Foodstuffs), the reliability of temperature-controlled equipment is paramount.
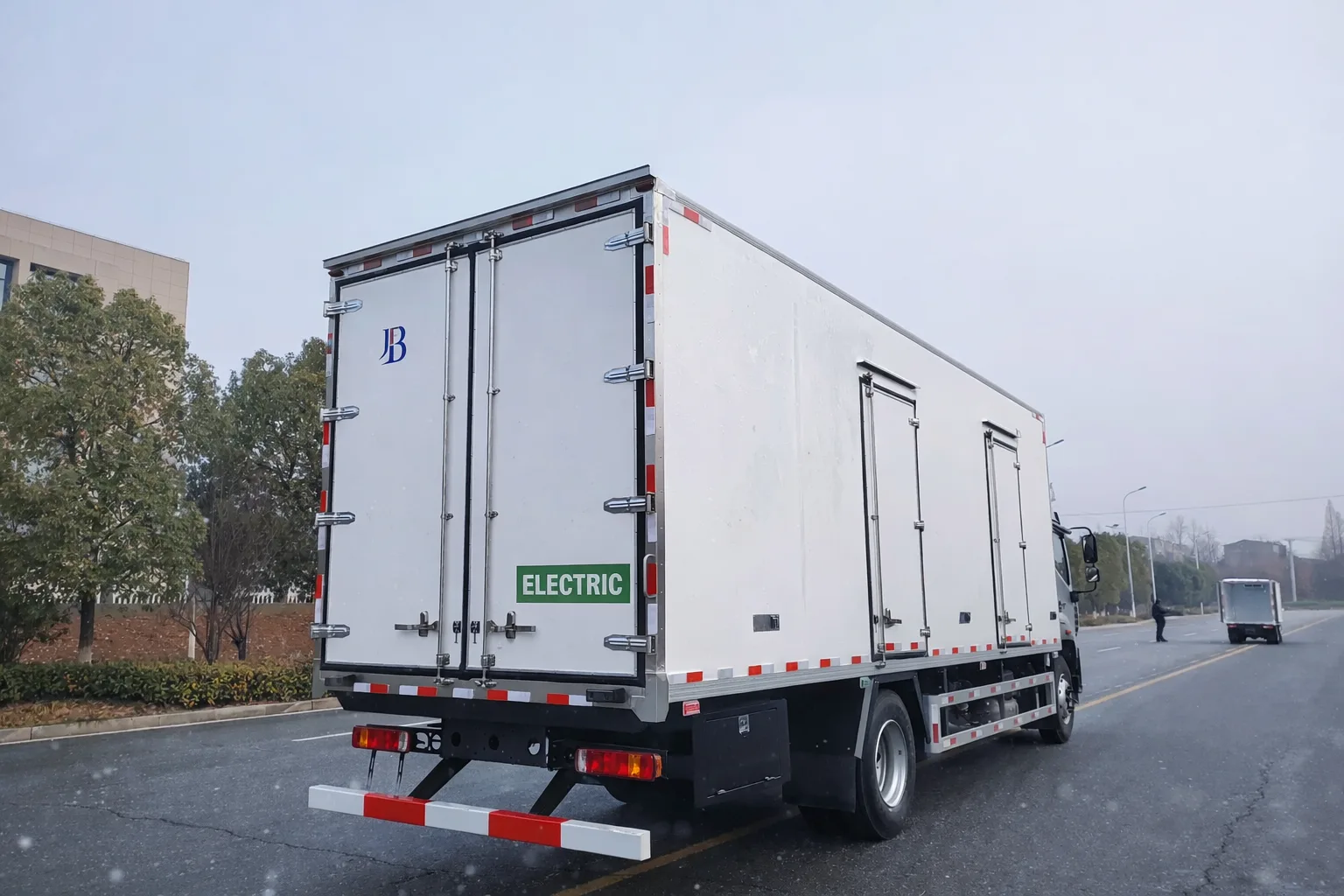

Walk-in Freezers and Commercial Cold Storage
- Recommended Material: Stainless Steel 304 or Steel Core with Engineering Plastic Coating.
- Environmental Challenge: Temperature ranges typically between -22°F to +39°F (-30°C to +4°C).
- Technical Rationale:
- Condensation Corrosion: Frequent door cycling causes condensation. 304 Stainless Steel passes the ASTM B117 neutral salt spray test for over 200 hours without red rust.
- Low-Temperature Toughness: Many metals become brittle at low temperatures (Ductile-to-Brittle Transition). Austenitic stainless steel retains high Charpy Impact Energy even at freezing temperatures, preventing fracture from accidental impacts.
Refrigerated Transport (Reefers) and Last-Mile Delivery
- Recommended Material: Extruded Aluminum Hinges.
- Market Trend:
- With the implementation of California’s CARB regulations, demand for Electric Refrigerated Trucks (EV Reefers) is surging.
- Every Pound Counts: Using an aluminum hinge system instead of traditional steel can shed approximately 45-65 lbs (20-30 kg) per truck. This directly translates to extended range for electric delivery vehicles.
- Durability Treatment:
- Due to road salt used for de-icing, automotive aluminum hinges must undergo Hard Anodizing. The coating thickness must reach 25-50 microns to resist road salt corrosion.
The Decision Matrix: Stainless Steel vs. Aluminum Performance Comparison (2026 Edition)
The table below summarizes key selection metrics. Use this as a reference for internal procurement audits.
| Comparison Metric | Stainless Steel (AISI 304/316) | Aluminum Alloy (6061 Anodized) | Winning Scenario |
| Tensile Strength | Very High (>515 MPa) | Medium (~310 MPa) | Heavy Duty / Explosion Proof Doors |
| Density (Weight) | Heavy (7.9 g/cm³) | Light (2.7 g/cm³) | Mobile Medical / EV Transport |
| Acid/Alkali Resistance | Excellent (Especially 316) | Poor (Vulnerable to Alkalis) | OR Sterilization / Chemical Washdown |
| Salt Spray Resistance (ASTM B117) | > 500 Hours (316) | > 336 Hours (Sealed) | Marine / Coastal Cold Storage |
| Low-Temp Impact | Excellent (No cold embrittlement) | Good | Deep Freeze Storage (Below -40°F) |
| Initial Cost | High ($$$) | Medium ($$) | Budget-Sensitive Projects |
| Machining Flexibility | Difficult (High Tooling Cost) | Easy (Flexible Extrusion) | Custom Design / Prototyping |
2026 Procurement Trends: Beyond the Material
Based on our discussions with major North American OEMs over the past week, three trends are reshaping hinge procurement strategies.
The Rise of Hybrid Hinges
To balance strength and weight, more designs are adopting a “Stainless Pin + Aluminum Leaf” structure.
- The Pin: Bears the primary shear force, utilizing 304 Stainless Steel.
- The Leaf: Provides connection surface area, utilizing Aluminum to save weight.
- Advantage: This combination retains 90% of the strength while reducing weight by 40%.
Evolution of Surface Treatment: PVD Coating
Traditional anodizing sometimes fails to meet extreme corrosion requirements. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) technology is now being introduced into high-end aluminum hinges.
- PVD coating forms an extremely dense protective film on the aluminum surface.
- This allows aluminum hinges to pass 1,000-hour salt spray tests, approaching the performance of stainless steel while maintaining a lightweight profile.
Supply Chain Resilience and “Made in USA”
Considering the volatility of global Nickel prices (a key component of stainless steel), many US buyers are pivoting to Aluminum.
- North America has a stable supply of Bauxite and a robust aluminum recycling supply chain.
- Sourcing aluminum products helps mitigate supply chain risks associated with geopolitical instability.
Conclusion and Engineering Recommendations
In the industrial environment of 2026, there is no “perfect” metal—only the most suitable choice for your specific operating conditions.
Our Engineering Summary:
- Choose AISI 316 Stainless Steel: If your equipment operates in highly corrosive, high-hygiene (Medical), or extreme heavy-load environments. It is the only choice to ensure compliance and durability.
- Choose Anodized Aluminum: If your equipment requires mobility, energy efficiency (Cold Chain Transport), or is weight-sensitive. This is the best path to achieve lightweighting and cost-efficiency.